Src-family kinases stabilize the neuromuscular synapse in vivo via protein interactions, phosphorylation, and cytoskeletal linkage of acetylcholine receptors
- PMID: 16280586
- PMCID: PMC6725837
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2103-05.2005
Src-family kinases stabilize the neuromuscular synapse in vivo via protein interactions, phosphorylation, and cytoskeletal linkage of acetylcholine receptors
Abstract
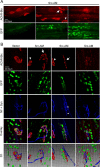
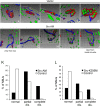
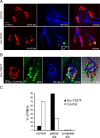
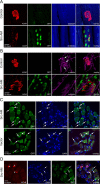
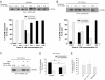
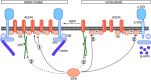
Postnatal stabilization and maturation of the postsynaptic membrane are important for development and function of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ), but the underlying mechanisms remain poorly characterized. We examined the role of Src-family kinases (SFKs) in vivo. Electroporation of kinase-inactive Src constructs into soleus muscles of adult mice caused NMJ disassembly: acetylcholine receptor (AChR)-rich areas became fragmented; the topology of nerve terminal, AChRs, and synaptic nuclei was disturbed; and occasionally nerves started to sprout. Electroporation of kinase-overactive Src produced similar but milder effects. We studied the mechanism of SFK action using cultured src(-/-);fyn(-/-) myotubes, focusing on clustering of postsynaptic proteins, their interaction with AChRs, and AChR phosphorylation. Rapsyn and the utrophin-glycoprotein complex were recruited normally into AChR-containing clusters by agrin in src(-/-);fyn(-/-) myotubes. But after agrin withdrawal, clusters of these proteins disappeared rapidly in parallel with AChRs, revealing that SFKs are of general importance in postsynaptic stability. At the same time, AChR interaction with rapsyn and dystrobrevin and AChR phosphorylation decreased after agrin withdrawal from mutant myotubes. Unexpectedly, levels of rapsyn protein were increased in src(-/-);fyn(-/-) myotubes, whereas rapsyn-cytoskeleton interactions were unaffected. The overall cytoskeletal link of AChRs was weak but still strengthened by agrin in mutant cells, consistent with the normal formation but decreased stability of AChR clusters. These data show that correctly balanced activity of SFKs is critical in maintaining adult NMJs in vivo. SFKs hold the postsynaptic apparatus together through stabilization of AChR-rapsyn interaction and AChR phosphorylation. In addition, SFKs control rapsyn levels and AChR-cytoskeletal linkage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tyrosine phosphatases such as SHP-2 act in a balance with Src-family kinases in stabilization of postsynaptic clusters of acetylcholine receptors.BMC Neurosci. 2007 Jul 2;8:46. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-8-46. BMC Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17605785 Free PMC article.
-
Laminin-1 redistributes postsynaptic proteins and requires rapsyn, tyrosine phosphorylation, and Src and Fyn to stably cluster acetylcholine receptors.J Cell Biol. 2002 May 27;157(5):883-95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200202110. Epub 2002 May 28. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12034776 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of rapsyn and agrin in interaction of postsynaptic proteins with acetylcholine receptors.J Neurosci. 1999 Aug 1;19(15):6405-16. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-15-06405.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10414969 Free PMC article.
-
The postsynaptic submembrane machinery at the neuromuscular junction: requirement for rapsyn and the utrophin/dystrophin-associated complex.J Neurocytol. 2003 Jun-Sep;32(5-8):709-26. doi: 10.1023/B:NEUR.0000020619.24681.2b. J Neurocytol. 2003. PMID: 15034263 Review.
-
Clustering of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: from the neuromuscular junction to interneuronal synapses.Mol Neurobiol. 2002 Feb;25(1):79-112. doi: 10.1385/MN:25:1:079. Mol Neurobiol. 2002. PMID: 11890459 Review.
Cited by
-
A histone deacetylase 4/myogenin positive feedback loop coordinates denervation-dependent gene induction and suppression.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Feb;20(4):1120-31. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-07-0759. Epub 2008 Dec 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19109424 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor Agonists Enhance AChR Clustering in C2C12 Myotubes: Implications for Therapy of Myasthenic Disorders.J Neuromuscul Dis. 2018;5(2):231-240. doi: 10.3233/JND-170293. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2018. PMID: 29865088 Free PMC article.
-
Protein networking: nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and their protein-protein-associations.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Jul;479(7):1627-1642. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05032-x. Epub 2024 May 21. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38771378 Review.
-
PICK1 interacts with alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and controls their clustering.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2007 Jun;35(2):339-55. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2007.03.009. Epub 2007 Mar 24. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17467288 Free PMC article.
-
Early gene expression changes in skeletal muscle from SOD1(G93A) amyotrophic lateral sclerosis animal model.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Apr;34(3):451-62. doi: 10.1007/s10571-014-0029-x. Epub 2014 Jan 18. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24442855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apel ED, Merlie JP (1995) Assembly of the postsynaptic apparatus. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5: 62-67. - PubMed
-
- Apel ED, Roberds SL, Campbell KP, Merlie JP (1995) Rapsyn may function as a link between the acetylcholine receptor and the agrin-binding dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex. Neuron 15: 115-126. - PubMed
-
- Bartoli M, Ramarao MK, Cohen JB (2001) Interactions of the rapsyn RING-H2 domain with dystroglycan. J Biol Chem 276: 24911-24917. - PubMed
-
- Bezakova G, Ruegg MA (2003) New insights into the roles of agrin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 295-308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
