Resistance to friend virus-induced erythroleukemia in W/W(v) mice is caused by a spleen-specific defect which results in a severe reduction in target cells and a lack of Sf-Stk expression
- PMID: 16282458
- PMCID: PMC1287579
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.23.14586-14594.2005
Resistance to friend virus-induced erythroleukemia in W/W(v) mice is caused by a spleen-specific defect which results in a severe reduction in target cells and a lack of Sf-Stk expression
Abstract
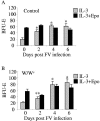
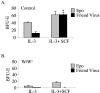
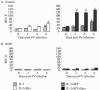
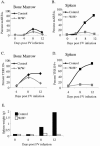
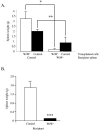
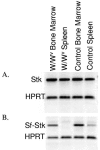
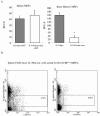
The characteristic progression and specificity of Friend virus for the erythroid lineage have allowed for the identification of a number of host-encoded loci that are required for disease progression. Several of these loci, including the Friend virus susceptibility gene 2 (Fv2), dominant white spotting gene (W), and Steel gene (Sl), regulate the initial polyclonal expansion of infected erythroid progenitor cells. W and Sl encode the Kit receptor tyrosine kinase and its ligand, stem cell factor, respectively. W mutant mice are severely anemic, and earlier work suggested that this defect in erythroid differentiation is the cause for the resistance to Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia. Here we show that in bone marrow, W/W(v) mice have near normal numbers of target cells and the initial infection of bone marrow occurs normally in vivo. In contrast, spleen cells from W/W(v) mice infected both in vitro and in vivo with Friend virus failed to give rise to erythropoietin-independent colonies at any time following Friend virus infection, suggesting that mutation of the Kit receptor specifically affects target cells in the spleen, rendering the mutant mice resistant to the development of Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia. In addition, we show that the Kit+ pathogenic targets of Friend virus in the spleen are distinct from the pathogenic targets in bone marrow and this population of spleen target cells is markedly decreased in W/W(v) mice and these cells fail to express Sf-Stk. These results also underscore the unique nature of the spleen microenvironment in its role in supporting the progression of acute leukemia in Friend virus-infected mice.
Figures
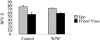

Similar articles
-
Sf-Stk kinase activity and the Grb2 binding site are required for Epo-independent growth of primary erythroblasts infected with Friend virus.Oncogene. 2002 May 16;21(22):3562-70. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205442. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12032858
-
Mutation of the Lyn tyrosine kinase delays the progression of Friend virus induced erythroleukemia without affecting susceptibility.Leuk Res. 2006 Sep;30(9):1141-9. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2006.02.006. Epub 2006 Mar 9. Leuk Res. 2006. PMID: 16527351
-
Ex vivo and in vivo biological effects of a truncated form of the receptor tyrosine kinase stk when activated by interaction with the friend spleen focus-forming virus envelope glycoprotein or by point mutation.J Virol. 2004 May;78(9):4573-81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.9.4573-4581.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15078939 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular regulation of receptor tyrosine kinases in hematopoietic malignancies.Gene. 2006 Jun 7;374:26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.01.023. Epub 2006 Mar 9. Gene. 2006. PMID: 16524673 Review.
-
The kit-ligand (steel factor) and its receptor c-kit/W: pleiotropic roles in gametogenesis and melanogenesis.Dev Suppl. 1993:125-37. Dev Suppl. 1993. PMID: 7519481 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of the N-terminally truncated form of the Stk receptor tyrosine kinase Sf-Stk by Friend virus-encoded gp55 is mediated by cysteine residues in the ecotropic domain of gp55 and the extracellular domain of Sf-Stk.J Virol. 2010 Mar;84(5):2223-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02090-09. Epub 2009 Dec 16. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20016000 Free PMC article.
-
Δ12-prostaglandin J3, an omega-3 fatty acid-derived metabolite, selectively ablates leukemia stem cells in mice.Blood. 2011 Dec 22;118(26):6909-19. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-11-317750. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21967980 Free PMC article.
-
A novel Stat3 binding motif in Gab2 mediates transformation of primary hematopoietic cells by the Stk/Ron receptor tyrosine kinase in response to Friend virus infection.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 May;27(10):3708-15. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01838-06. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17353274 Free PMC article.
-
BMP4, SCF, and hypoxia cooperatively regulate the expansion of murine stress erythroid progenitors.Blood. 2007 May 15;109(10):4494-502. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-016154. Epub 2007 Feb 6. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17284534 Free PMC article.
-
Spi-1 and Fli-1 directly activate common target genes involved in ribosome biogenesis in Friend erythroleukemic cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 May;29(10):2852-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01435-08. Epub 2009 Mar 16. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19289502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afrikanova, I., E. Yeh, D. Bartos, S. Watowich, and G. Longmore. 2002. Oncogene cooperativity in Friend erythroleukemia: erythropoietin receptor activation by the env gene of SFFV leads to transcriptional upregulation of PU.1, independent of SFFV proviral insertion. Oncogene 21:1272-1284. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akashi, K., D. Traver, T. Miyamoto, and I. Weissman. 2000. A clonogenic common myeloid progenitor that gives rise to all myeloid lineages. Nature 404:193-197. - PubMed
-
- Ashman, L. K. 1999. The biology of stem cell factor and its receptor c-Kit. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 31:1037-1051. - PubMed
-
- Axelrad, A. 1969. Genetic and cellular basis of susceptibility or resistance to Friend leukemia virus infection in mice. Proc. Can. Cancer Conf. 8:313-343. - PubMed
-
- Baumann, C. I., A. S. Bailey, W. Li, M. J. Ferkowicz, M. C. Yoder, and W. H. Fleming. 2004. PECAM-1 is expressed on hematopoietic stem cells throughout ontogeny and identifies a population of erythroid progenitors. Blood 104:1010-1016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

