Breaking an absolute species barrier: transgenic mice expressing the mink PrP gene are susceptible to transmissible mink encephalopathy
- PMID: 16282497
- PMCID: PMC1287601
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.23.14971-14975.2005
Breaking an absolute species barrier: transgenic mice expressing the mink PrP gene are susceptible to transmissible mink encephalopathy
Abstract
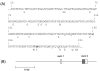
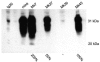
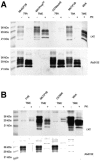
Transmissible mink encephalopathy (TME) is a rare disease of the North American mink, which has never been successfully transmitted to laboratory mice. We generated transgenic mice expressing the mink prion protein (PrP) and inoculated them with TME or the mouse-adapted scrapie strain 79A. TME infected mink PrP-transgenic mice on a murine PrP knockout background. The absolute species barrier between the infectious agent of TME and mice was therefore broken. Following TME and 79A infection of mice carrying both mink and murine PrP(C), only proteinase-resistant PrP homologous to the incoming agent was detectable. The presence of the murine PrP(C) prolonged the incubation time of TME substantially.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sc237 hamster PrPSc and Sc237-derived mouse PrPSc generated by interspecies in vitro amplification exhibit distinct pathological and biochemical properties in tga20 transgenic mice.Microbiol Immunol. 2011 May;55(5):331-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2011.00328.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21362027
-
Raccoons accumulate PrPSc after intracranial inoculation of the agents of chronic wasting disease or transmissible mink encephalopathy but not atypical scrapie.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2019 Mar;31(2):200-209. doi: 10.1177/1040638718825290. Epub 2019 Jan 29. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2019. PMID: 30694116 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-associated prion protein in neural and lymphoid tissues of mink (Mustela vison) inoculated with transmissible mink encephalopathy.J Comp Pathol. 2012 Nov;147(4):508-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2012.03.008. Epub 2012 May 16. J Comp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22595634 Free PMC article.
-
Prion encephalopathies of animals and humans.Dev Biol Stand. 1993;80:31-44. Dev Biol Stand. 1993. PMID: 8270114 Review.
-
[Mechanisms of neuroinvasion by prions: molecular principles and present state of research].Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 2000 Mar 25;130(12):435-42. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 2000. PMID: 10780058 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Cross currents in protein misfolding disorders: interactions and therapy.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2009 Nov;8(5):363-71. doi: 10.2174/187152709789541998. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19702573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prion replication without host adaptation during interspecies transmissions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jan 31;114(5):1141-1146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611891114. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28096357 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing Prion Proteins Across Species: Is Zebrafish a Useful Model?Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jan;62(1):832-845. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04324-z. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 38918277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenic Rabbits Expressing Ovine PrP Are Susceptible to Scrapie.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Aug 6;11(8):e1005077. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005077. eCollection 2015 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26248157 Free PMC article.
-
The prion hypothesis: from biological anomaly to basic regulatory mechanism.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;11(12):823-33. doi: 10.1038/nrm3007. Epub 2010 Nov 17. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 21081963 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bessen, R. A., and R. F. Marsh. 1992. Identification of two biologically distinct strains of transmissible mink encephalopathy in hamsters. J. Gen. Virol. 73:329-334. - PubMed
-
- Bruce, M. E., P. A. McBride, M. Jeffrey, and J. R. Scott. 1994. PrP in pathology and pathogenesis in scrapie-infected mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 8:105-112. - PubMed
-
- Büeler, H., M. Fischer, Y. Lang, H. Bluethmann, H. P. Lipp, S. J. DeArmond, S. B. Prusiner, M. Aguet, and C. Weissmann. 1992. Normal development and behaviour of mice lacking the neuronal cell-surface PrP protein. Nature 356:577-582. - PubMed
-
- Buschmann, A., E. Pfaff, K. Reifenberg, H. M. Muller, and M. H. Groschup. 2000. Detection of cattle-derived BSE prions using transgenic mice-overexpressing bovine PrP(c). Arch. Virol. Suppl. 16:75-86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

