Neutrophilic inflammation and IL-8 levels in induced sputum of alpha-1-antitrypsin PiMZ subjects
- PMID: 16284217
- PMCID: PMC2104580
- DOI: 10.1136/thx.2005.043471
Neutrophilic inflammation and IL-8 levels in induced sputum of alpha-1-antitrypsin PiMZ subjects
Abstract
Background: Severe alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency (AATD), due to homozygosity for the protease inhibitor (Pi) Z allele, is a genetic risk factor for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In a previous study the sputum of severe AATD subjects with airflow obstruction showed a pattern of cellular inflammation similar to COPD patients. It is uncertain whether heterozygotes for the Z allele or intermediate deficiency (PiMZ) have an increased risk of developing COPD.
Methods: Sputum cell counts and the supernatant level of the neutrophil chemoattractant interleukin (IL)-8 were investigated by sputum induction in 10 non-smoker asymptomatic PiMZ subjects with normal pulmonary function, 10 patients with stable COPD, and 10 age matched normal subjects. Data are expressed as mean (SD).
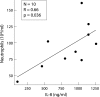
Results: The mean (SD) number of neutrophils was significantly higher (p<0.01) in the sputum of PiMZ subjects (84.5 (22.2) x10(4)/ml) and patients with COPD (126.9 (18.8) x10(4)/ml) than in matched normal subjects (55.0 (8.7) x10(4)/ml). IL-8 levels were increased in PiMZ subjects (828.5 (490.6) ng/ml; median 1003.0 ng/ml; range 1260-100 ng/ml) and in COPD patients (882.5 (524.3) ng/ml; median 934.9 ng/ml; range 1506-258 mg/ml) compared with normal subjects (3.5 (0.5) ng/ml; median 3.5 ng/ml; range 4.5-2.5 ng/ml). There was a significant positive correlation between IL-8 supernatant concentration and neutrophil count in PiMZ subjects (p = 0.036; r = 0.66). An inverse correlation was observed between the percentage of neutrophils and forced expiratory volume in 1 second (% predicted) in patients with COPD (p = 0.04; r = -0.43).
Conclusions: These findings indicate that PiMZ subjects without airflow obstruction may have an IL-8 related neutrophilic inflammation in the airways, similar to stable COPD patients, suggesting an increased risk of developing pulmonary changes.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none declared.
References
-
- Aboussuan L S, Stoller J K. New developments in alpha 1‐antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 199920301–310.
-
- American Thoracic Society Guidelines for the approach to the patient with severe hereditary alpha‐1‐antitrypsin deficiency. Am Rev Respir Dis 198940494–497. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous