Reduced mitochondrial density and increased IRS-1 serine phosphorylation in muscle of insulin-resistant offspring of type 2 diabetic parents
- PMID: 16284649
- PMCID: PMC1280967
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI25151
Reduced mitochondrial density and increased IRS-1 serine phosphorylation in muscle of insulin-resistant offspring of type 2 diabetic parents
Abstract
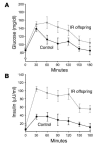
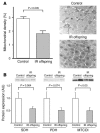
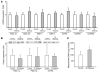
To further explore the nature of the mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance that occur in the muscle of young, lean, normoglycemic, insulin-resistant offspring of parents with type 2 diabetes (IR offspring), we measured mitochondrial content by electron microscopy and insulin signaling in muscle biopsy samples obtained from these individuals before and during a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp. The rate of insulin-stimulated muscle glucose uptake was approximately 60% lower in the IR offspring than the control subjects and was associated with an approximately 60% increase in the intramyocellular lipid content as assessed by H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Muscle mitochondrial density was 38% lower in the IR offspring. These changes were associated with a 50% increase in IRS-1 Ser312 and IRS-1 Ser636 phosphorylation and an approximately 60% reduction in insulin-stimulated Akt activation in the IR offspring. These data provide new insights into the earliest defects that may be responsible for the development of type 2 diabetes and support the hypothesis that reductions in mitochondrial content result in decreased mitochondrial function, which predisposes IR offspring to intramyocellular lipid accumulation, which in turn activates a serine kinase cascade that leads to defects in insulin signaling and action in muscle.
Figures

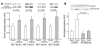
References
-
- Griffin ME, et al. Free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance is associated with activation of protein kinase C theta and alterations in the insulin signaling cascade. Diabetes. 1999;48:1270–1274. - PubMed
-
- Yu C, et al. Mechanism by which fatty acids inhibit insulin activation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1)-associated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:50230–50236. - PubMed
-
- Itani SI, Ruderman NB, Schmieder F, Boden G. Lipid-induced insulin resistance in human muscle is associated with changes in diacylglycerol, protein kinase C, and IkappaB-alpha. Diabetes. 2002;51:2005–2011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK049230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK068229/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK-45735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK-063192/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK040936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023686/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK-49230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR-00125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK-68229/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG-23686/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

