Prediction discrepancies for the evaluation of nonlinear mixed-effects models
- PMID: 16284919
- PMCID: PMC1989778
- DOI: 10.1007/s10928-005-0016-4
Prediction discrepancies for the evaluation of nonlinear mixed-effects models
Abstract
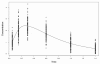
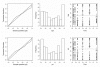
Reliable estimation methods for non-linear mixed-effects models are now available and, although these models are increasingly used, only a limited number of statistical developments for their evaluation have been reported. We develop a criterion and a test to evaluate nonlinear mixed-effects models based on the whole predictive distribution. For each observation, we define the prediction discrepancy (pd) as the percentile of the observation in the whole marginal predictive distribution under H(0). We propose to compute prediction discrepancies using Monte Carlo integration which does not require model approximation. If the model is valid, these pd should be uniformly distributed over (0, 1) which can be tested by a Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. In a simulation study based on a standard population pharmacokinetic model, we compare and show the interest of this criterion with respect to the one most frequently used to evaluate nonlinear mixed-effects models: standardized prediction errors (spe) which are evaluated using a first order approximation of the model. Trends in pd can also be evaluated via several plots to check for specific departures from the model.
Figures


References
-
- Sheiner LB, Steimer JL. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling in drug development. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2000;40:67–95. - PubMed
-
- Aarons L, Karlsson MO, Mentré F, Rombout F, Steimer JL, van Peer A. Cost B15 experts. Role of modelling and simulation in phase I drug development. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2001;13:115–122. - PubMed
-
- Holford NH, Kimko HC, Monteleone JP, Peck CC. Simulation of clinical trials. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2000;40:209–234. - PubMed
-
- Lesko LJ, Rowland M, Peck CC, Blaschke TF. Optimizing the science of drug development: opportunities for better candidate selection and accelerated evaluations in humans. J Clin Pharmacol. 2000;40:803–814. - PubMed
-
- Kimko HC, Duffull SB. Simulation for designing clinical trials: a pharmacokinetic - pharmacodynamic modeling prospective. Marcel Dekker; New York: 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

