In vitro selection, characterization, and application of deoxyribozymes that cleave RNA
- PMID: 16286368
- PMCID: PMC1283523
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki930
In vitro selection, characterization, and application of deoxyribozymes that cleave RNA
Abstract
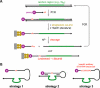
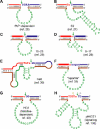
Over the last decade, many catalytically active DNA molecules (deoxyribozymes; DNA enzymes) have been identified by in vitro selection from random-sequence DNA pools. This article focuses on deoxyribozymes that cleave RNA substrates. The first DNA enzyme was reported in 1994 and cleaves an RNA linkage. Since that time, many other RNA-cleaving deoxyribozymes have been identified. Most but not all of these deoxyribozymes require a divalent metal ion cofactor such as Mg2+ to catalyze attack by a specific RNA 2'-hydroxyl group on the adjacent phosphodiester linkage, forming a 2',3'-cyclic phosphate and a 5'-hydroxyl group. Several deoxyribozymes that cleave RNA have utility for in vitro RNA biochemistry. Some DNA enzymes have been applied in vivo to degrade mRNAs, and others have been engineered into sensors. The practical impact of RNA-cleaving deoxyribozymes should continue to increase as additional applications are developed.
Figures
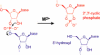
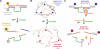
References
-
- Doudna J.A., Cech T.R. The chemical repertoire of natural ribozymes. Nature. 2002;418:222–228. - PubMed
-
- Collins C.A., Guthrie C. The question remains: is the spliceosome a ribozyme? Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000;7:850–854. - PubMed
-
- Villa T., Pleiss J.A., Guthrie C. Spliceosomal snRNAs: Mg2+-dependent chemistry at the catalytic core? Cell. 2002;109:149–152. - PubMed
-
- Ban N., Nissen P., Hansen J., Moore P.B., Steitz T.A. The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science. 2000;289:905–920. - PubMed
-
- Cech T.R. The ribosome is a ribozyme. Science. 2000;289:878–879. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

