The ER aminopeptidase, ERAP1, trims precursors to lengths of MHC class I peptides by a "molecular ruler" mechanism
- PMID: 16286653
- PMCID: PMC1287962
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0500721102
The ER aminopeptidase, ERAP1, trims precursors to lengths of MHC class I peptides by a "molecular ruler" mechanism
Abstract
Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) is an IFN-gamma-induced aminopeptidase in the endoplasmic reticulum that trims longer precursors to the antigenic peptides presented on MHC class I molecules. We recently reported that purified ERAP1 trimmed N-extended precursors but spared peptides of 8-9 residues, the length required for binding to MHC class I molecules. Here, we show another remarkable property of ERAP1: that it strongly prefers substrates 9-16 residues long, the lengths of peptides transported efficiently into the ER by the transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) transporter. This aminopeptidase rapidly degraded a model 13-mer to a 9-mer and then stopped, even though the substrate and the product had identical N- and C-terminal sequences. No other aminopeptidase, including the closely related ER-aminopeptidase ERAP2, showed a similar length preference. Unlike other aminopeptidases, the activity of ERAP1 depended on the C-terminal residue of the substrate. ERAP1, like most MHC class I molecules, prefers peptides with hydrophobic C termini and shows low affinity for peptides with charged C termini. Thus, ERAP1 is specialized to process precursors transported by TAP to peptides that can serve as MHC class I epitopes. Its "molecular ruler" mechanism involves binding the hydrophobic C terminus of the substrate 9-16 residues away from the active site.
Figures

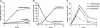



References
-
- Rock, K. L. & Goldberg, A. L. (1999) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17, 739-779. - PubMed
-
- Yewdell, J. W. & Bennink, J. R. (2001) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 13, 13-18. - PubMed
-
- Shastri, N., Schwab, S. & Serwold, T. (2002) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 463-493. - PubMed
-
- Rock, K. L., York, I. A., Saric, T. & Goldberg, A. L. (2002) Adv. Immunol. 80, 1-70. - PubMed
-
- Madden, D. R. (1995) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 13, 587-622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

