A Brg1 mutation that uncouples ATPase activity from chromatin remodeling reveals an essential role for SWI/SNF-related complexes in beta-globin expression and erythroid development
- PMID: 16287714
- PMCID: PMC1315392
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1364105
A Brg1 mutation that uncouples ATPase activity from chromatin remodeling reveals an essential role for SWI/SNF-related complexes in beta-globin expression and erythroid development
Abstract
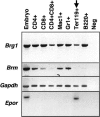
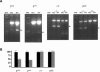
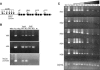
The Brg1 catalytic subunit of SWI/SNF-related complexes has been implicated in many developmental and physiological processes, but null homozygotes die as blastocysts prior to implantation. To circumvent this early embryonic lethality, we performed an ENU mutagenesis screen and generated a Brg1 hypomorph mutation in the ATPase domain. The mutant Brg1 protein is stable, assembles into SWI/SNF-related complexes, and exhibits normal ATPase activity but is unable to establish DNase I hypersensitivity sites characteristic of open chromatin. Mutant embryos develop normally until midgestation but then exhibit a distinct block in the development of the erythroid lineage, leading to anemia and death. The mutant Brg1 protein is recruited to the beta-globin locus, but chromatin remodeling and transcription are perturbed. Histone acetylation and DNA methylation are also affected. To our knowledge, Brg1 is the first chromatin-modifying factor shown to be required for beta-globin regulation and erythropoiesis in vivo. Not only does this mutation establish a role for Brg1 during organogenesis, it also demonstrates that ATPase activity can be uncoupled from chromatin remodeling.
Figures
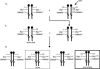




Similar articles
-
Characterization of a Brg1 hypomorphic allele demonstrates that genetic and biochemical activity are tightly correlated.Epigenetics. 2014 Feb;9(2):249-56. doi: 10.4161/epi.26879. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Epigenetics. 2014. PMID: 24172864 Free PMC article.
-
The chromatin-remodeling enzyme BRG1 plays an essential role in primitive erythropoiesis and vascular development.Development. 2008 Feb;135(3):493-500. doi: 10.1242/dev.010090. Epub 2007 Dec 19. Development. 2008. PMID: 18094026 Free PMC article.
-
Co-regulation of transcription by BRG1 and BRM, two mutually exclusive SWI/SNF ATPase subunits.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2017 Dec 22;10(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13072-017-0167-8. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2017. PMID: 29273066 Free PMC article.
-
The BRG1 ATPase of human SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling enzymes as a driver of cancer.Epigenomics. 2017 Jun;9(6):919-931. doi: 10.2217/epi-2017-0034. Epub 2017 May 19. Epigenomics. 2017. PMID: 28521512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research Progress on the Role of Chromatin Remodeling Factor BRG1 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Jun;24(3):930-3. doi: 10.7534/j.issn.1009-2137.2016.03.054. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27342536 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Brg1 Controls the Expression of Pax7 to Promote Viability and Proliferation of Mouse Primary Myoblasts.J Cell Physiol. 2015 Dec;230(12):2990-7. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25031. J Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26036967 Free PMC article.
-
Hemogen/BRG1 cooperativity modulates promoter and enhancer activation during erythropoiesis.Blood. 2022 Jun 16;139(24):3532-3545. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021014308. Blood. 2022. PMID: 35297980 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin-remodelling factor Brg1 regulates myocardial proliferation and regeneration in zebrafish.Nat Commun. 2016 Dec 8;7:13787. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13787. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27929112 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin remodelling during development.Nature. 2010 Jan 28;463(7280):474-84. doi: 10.1038/nature08911. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20110991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening for inhibitors of an essential chromatin remodeler in mouse embryonic stem cells by monitoring transcriptional regulation.J Biomol Screen. 2012 Oct;17(9):1221-30. doi: 10.1177/1087057112455060. Epub 2012 Aug 1. J Biomol Screen. 2012. PMID: 22853929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong, J.A., Bieker, J.J., and Emerson, B.M. 1998. A SWI/SNF-related chromatin remodeling complex, E-RC1, is required for tissue-specific transcriptional regulation by EKLF in vitro. Cell 95: 93-104. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., and Struhl, K. 1992. Current protocols in molecular biology. Greene Publishing Associates/Wiley Interscience, New York.
-
- Banine, F., Bartlett, C., Gunawardena, R., Muchardt, C., Yaniv, M., Knudsen, E.S., Weissman, B.E., and Sherman, L.S. 2005. SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling factors induce changes in DNA methylation to promote transcriptional activation. Cancer Res. 65: 3542-3547. - PubMed
-
- Bender, M.A., Reik, A., Close, J., Telling, A., Epner, E., Fiering, S., Hardison, R., and Groudine, M. 1998. Description and targeted deletion of 5′ hypersensitive site 5 and 6 of the mouse β-globin locus control region. Blood 92: 4394-4403. - PubMed
-
- Bultman, S., Gebuhr, T., Yee, D., La Mantia, C., Nicholson, J., Gilliam, A., Randazzo, F., Metzger, D., Chambon, P., Crabtree, G., et al. 2000. A Brg1 null mutation in the mouse reveals functional differences among mammalian SWI/SNF complexes. Mol. Cell 6: 1287-1295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
