Molecular mechanism of light responses in Neurospora: from light-induced transcription to photoadaptation
- PMID: 16287715
- PMCID: PMC1315395
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1369605
Molecular mechanism of light responses in Neurospora: from light-induced transcription to photoadaptation
Abstract
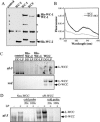
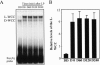
Blue light regulates many molecular and physiological activities in a large number of organisms. In Neurospora crassa, a eukaryotic model system for studying blue-light responses, the transcription factor and blue-light photoreceptor WHITE COLLAR-1 (WC-1) and its partner WC-2 are central to blue-light sensing. Neurospora's light responses are transient, that is, following an initial acute phase of induction, light-regulated processes are down-regulated under continuous illumination, a phenomenon called photoadaptation. The molecular mechanism(s) of photoadaptation are not well understood. Here we show that a common mechanism controls the light-induced transcription of immediate early genes (such as frq, al-3, and vvd) in Neurospora, in which light induces the binding of identical large WC-1/WC-2 complexes (L-WCC) to the light response elements (LREs) in their promoters. Using recombinant proteins, we show that the WC complexes are functional without the requirement of additional factors. In vivo, WCC has a long period photocycle, indicating that it cannot be efficiently used for repeated light activation. Contrary to previous expectations, we demonstrate that the light-induced hyperphosphorylation of WC proteins inhibits bindings of the L-WCC to the LREs. We show that, in vivo, due to its rapid hyperphosphorylation, L-WCC can only bind transiently to LREs, indicating that WCC hyperphosphorylation is a critical process for photoadaptation. Finally, phosphorylation was also shown to inhibit the LRE-binding activity of D-WCC (dark WC complex), suggesting that it plays an important role in the circadian negative feedback loop.
Figures





References
-
- Aronson, B., Johnson, K., Loros, J.J., and Dunlap, J.C. 1994. Negative feedback defining a circadian clock: Autoregulation in the clock gene frequency. Science 263: 1578-1584. - PubMed
-
- Arpaia, G., Carattoli, A., and Macino, G. 1995. Light and development regulate the expression of the albino-3 gene in Neurospora crassa. Dev. Biol. 170: 626-635. - PubMed
-
- Arpaia, G., Cerri, F., Baima, S., and Macino, G. 1999. Involvement of protein kinase C in the response of Neurospora crassa to blue light. Mol. Gen. Genet. 262: 314-322. - PubMed
-
- Baima, S., Macino, G., and Morelli, G. 1991. Photoregulation of the al-3 gene in Neurospora crassa. Photochem. Photobiol. 11: 107-115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
