Cholinergic septo-hippocampal innervation is required for trace eyeblink classical conditioning
- PMID: 16287719
- PMCID: PMC1356172
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.28105
Cholinergic septo-hippocampal innervation is required for trace eyeblink classical conditioning
Abstract
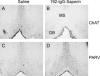
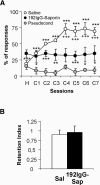
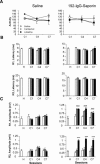
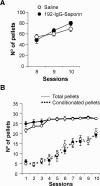
We studied the effects of a selective lesion in rats, with 192-IgG-saporin, of the cholinergic neurons located in the medial septum/diagonal band (MSDB) complex on the acquisition of classical and instrumental conditioning paradigms. The MSDB lesion induced a marked deficit in the acquisition, but not in the retrieval, of eyeblink classical conditioning using a trace paradigm. Such a deficit was task-selective, as lesioned rats were able to acquire a fixed-interval operant conditioning as controls, and was not due to nonspecific motor alterations, because spontaneous locomotion and blink reflexes were not disturbed by the MSDB lesion. The deficit in the acquisition of a trace eyeblink classical conditioning was reverted by the systemic administration of carbachol, a nonselective cholinergic muscarinic agonist, but not by lobeline, a nicotinic agonist. These results suggest a key role of muscarinic denervation on the acquisition of new motor abilities using trace classical conditioning procedures. It might also be suggested that muscarinic agents would be useful for the amelioration of some associative learning deficits observed at early stages in patients with Alzheimer's disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GABAergic neurons in the medial septum-diagonal band of Broca (MSDB) are important for acquisition of the classically conditioned eyeblink response.Brain Struct Funct. 2014 Jul;219(4):1231-7. doi: 10.1007/s00429-013-0560-4. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Brain Struct Funct. 2014. PMID: 24965560 Free PMC article.
-
Trace eyeblink conditioning is hippocampally dependent in mice.Hippocampus. 2004;14(1):58-65. doi: 10.1002/hipo.10157. Hippocampus. 2004. PMID: 15058483
-
A computational model of cholinergic disruption of septohippocampal activity in classical eyeblink conditioning.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 1996 Jul;66(1):51-66. doi: 10.1006/nlme.1996.0043. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 1996. PMID: 8661251 Review.
-
Ontogeny of septohippocampal modulation of delay eyeblink conditioning.Dev Psychobiol. 2015 Mar;57(2):168-76. doi: 10.1002/dev.21272. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Dev Psychobiol. 2015. PMID: 25604349 Free PMC article.
-
Functional basis of associative learning and its relationships with long-term potentiation evoked in the involved neural circuits: Lessons from studies in behaving mammals.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015 Oct;124:3-18. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2015.04.006. Epub 2015 Apr 25. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015. PMID: 25916668 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute and repeated effects of three organophosphorus pesticides on the acquisition and retention of an instrumental learning task in rats.Neurotox Res. 2008 May-Jun;13(3-4):253-63. doi: 10.1007/BF03033509. Neurotox Res. 2008. PMID: 18522905
-
Multiple sites of extinction for a single learned response.J Neurophysiol. 2012 Jan;107(1):226-38. doi: 10.1152/jn.00381.2011. Epub 2011 Sep 21. J Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 21940608 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Roles of Somatostatin and Parvalbumin Interneurons in Regulating Predictive Actions and Emotional Responses During Trace Eyeblink Conditioning.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 24:2025.03.23.644831. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.23.644831. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40196611 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
An experimental model for the study of cognitive disorders: the hippocampus and associative learning in mice.Neurotox Res. 2008 Dec;14(4):359-66. doi: 10.1007/BF03033860. Neurotox Res. 2008. PMID: 19073439
-
Involvement of the CA3-CA1 synapse in the acquisition of associative learning in behaving mice.J Neurosci. 2006 Jan 25;26(4):1077-87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2834-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16436593 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartus, R.T., Dean III R.L., Beer, B., and Lippa, A.S. 1982. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science 217: 408-414. - PubMed
-
- Baxter, M.G. and Chiba, A.A. 1999. Cognitive functions of the basal forebrain. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 9: 178-183. - PubMed
-
- Baxter, M.G., Bucci, D.J., Sobel, T.J., Williams, M.J., Gorman, L.K., and Gallagher, M. 1996. Intact spatial learning following lesions of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Neuroreport 7: 1417-1420. - PubMed
-
- Berry, S.D. and Thompson, R.F. 1979. Medial septal lesions retard classical conditioning of the nictitating membrane response in rabbits. Science 205: 209-211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
