The hematopoietic transcription factor AML1 (RUNX1) is negatively regulated by the cell cycle protein cyclin D3
- PMID: 16287839
- PMCID: PMC1291252
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.23.10205-10219.2005
The hematopoietic transcription factor AML1 (RUNX1) is negatively regulated by the cell cycle protein cyclin D3
Abstract
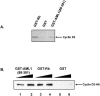
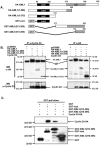
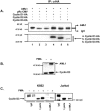
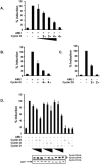
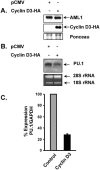
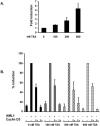
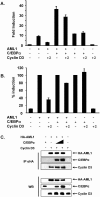
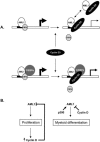
The family of cyclin D proteins plays a crucial role in the early events of the mammalian cell cycle. Recent studies have revealed the involvement of AML1 transactivation activity in promoting cell cycle progression through the induction of cyclin D proteins. This information in combination with our previous observation that a region in AML1 between amino acids 213 and 289 is important for its function led us to investigate prospective proteins associating with this region. We identified cyclin D3 by a yeast two-hybrid screen and detected AML1 interaction with the cyclin D family by both in vitro pull-down and in vivo coimmunoprecipitation assays. Furthermore, we demonstrate that cyclin D3 negatively regulates the transactivation activity of AML1 in a dose-dependent manner by competing with CBFbeta for AML1 association, leading to a decreased binding affinity of AML1 for its target DNA sequence. AML1 and its fusion protein AML1-ETO have been shown to shorten and prolong the mammalian cell cycle, respectively. In addition, AML1 promotes myeloid cell differentiation. Thus, our observations suggest that the direct association of cyclin D3 with AML1 functions as a putative feedback mechanism to regulate cell cycle progression and differentiation.
Figures


References
-
- Bates, S., and G. Peters. 1995. Cyclin D1 as a cellular proto-oncogene. Semin. Cancer Biol. 6:73-82. - PubMed
-
- Behre, G., P. Zhang, D. E. Zhang, and D. G. Tenen. 1999. Analysis of the modulation of transcriptional activity in myelopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Methods 17:231-237. - PubMed
-
- Bernardin, F., and A. D. Friedman. 2002. AML1 stimulates G1 to S progression via its transactivation domain. Oncogene 21:3247-3252. - PubMed
-
- Bernardin-Fried, F., T. Kummalue, S. Leijen, M. I. Collector, K. Ravid, and A. D. Friedman. 2004. AML1/RUNX1 increases during G1 to S cell cycle progression independent of cytokine-dependent phosphorylation and induces cyclin D3 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 279:15678-15687. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
