Generation and characterization of p38beta (MAPK11) gene-targeted mice
- PMID: 16287858
- PMCID: PMC1291241
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.23.10454-10464.2005
Generation and characterization of p38beta (MAPK11) gene-targeted mice
Abstract
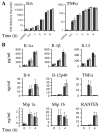
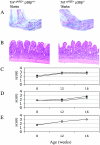
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are activated primarily in response to inflammatory cytokines and cellular stress, and inhibitors which target the p38alpha and p38beta MAPKs have shown potential for the treatment of inflammatory disease. Here we report the generation and initial characterization of a knockout of the p38beta (MAPK11) gene. p38beta-/- mice were viable and exhibited no apparent health problems. The expression and activation of p38alpha, ERK1/2, and JNK in response to cellular stress was normal in embryonic fibroblasts from p38beta-/- mice, as was the activation of p38-activated kinases MAPKAP-K2 and MSK1. The transcription of p38-dependent immediate-early genes was also not affected by the knockout of p38beta, suggesting that p38alpha is the predominant isoform involved in these processes. The p38beta-/- mice also showed normal T-cell development. Lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine production was also normal in the p38beta-/- mice. As p38 is activated by tumor necrosis factor, the p38beta-/- mice were crossed onto a TNFDeltaARE mouse line. These mice overexpress tumor necrosis factor, which results in development symptoms similar to rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. The progression of these diseases was not however moderated by knockout of p38beta. Together these results suggest that p38alpha, and not p38beta, is the major p38 isoform involved in the immune response and that it would not be necessary to retain activity against p38beta during the development of p38 inhibitors.
Figures





References
-
- Adams, R. H., A. Porras, G. Alonso, M. Jones, K. Vintersten, S. Panelli, A. Valladares, L. Perez, R. Klein, and A. R. Nebreda. 2000. Essential role of p38alpha MAP kinase in placental but not embryonic cardiovascular development. Mol. Cell 6:109-116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
