Inactivation of Ku-mediated end joining suppresses mec1Delta lethality by depleting the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor Sml1 through a pathway controlled by Tel1 kinase and the Mre11 complex
- PMID: 16287875
- PMCID: PMC1291227
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.23.10652-10664.2005
Inactivation of Ku-mediated end joining suppresses mec1Delta lethality by depleting the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor Sml1 through a pathway controlled by Tel1 kinase and the Mre11 complex
Abstract
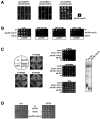
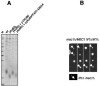
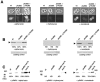
RAD53 and MEC1 are essential Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes required for the DNA replication and DNA damage checkpoint responses. Their lethality can be suppressed by increasing the intracellular pool of deoxynucleotide triphosphates. We report that deletion of YKU70 or YKU80 suppresses mec1Delta, but not rad53Delta, lethality. We show that suppression of mec1Delta lethality is not due to Ku--associated telomeric defects but rather results from the inability of Ku- cells to efficiently repair DNA double strand breaks by nonhomologous end joining. Consistent with these results, mec1Delta lethality is also suppressed by lif1Delta, which like yku70Delta and yku80Delta, prevents nonhomologous end joining. The viability of yku70Delta mec1Delta and yku80Delta mec1Delta cells depends on the ATM-related Tel1 kinase, the Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2 complex, and the DNA damage checkpoint protein Rad9. We further report that this Mec1-independent pathway converges with the Rad53/Dun1-regulated checkpoint kinase cascade and leads to the degradation of the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor Sml1.
Figures

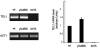
Similar articles
-
Requirement of the Mre11 complex and exonuclease 1 for activation of the Mec1 signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Nov;24(22):10016-25. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.22.10016-10025.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15509802 Free PMC article.
-
The Dun1 checkpoint kinase phosphorylates and regulates the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor Sml1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Mar 19;99(6):3746-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.062502299. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11904430 Free PMC article.
-
Sae2 antagonizes Rad9 accumulation at DNA double-strand breaks to attenuate checkpoint signaling and facilitate end resection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 18;115(51):E11961-E11969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816539115. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30510002 Free PMC article.
-
Interplays between ATM/Tel1 and ATR/Mec1 in sensing and signaling DNA double-strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2013 Oct;12(10):791-9. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2013.07.009. Epub 2013 Aug 13. DNA Repair (Amst). 2013. PMID: 23953933 Review.
-
Rad50S alleles of the Mre11 complex: questions answered and questions raised.Exp Cell Res. 2006 Aug 15;312(14):2694-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.06.013. Epub 2006 Jun 20. Exp Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16857186 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential regulation of the cellular response to DNA double-strand breaks in G1.Mol Cell. 2008 Apr 11;30(1):73-85. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.01.016. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18406328 Free PMC article.
-
Mec1p associates with functionally compromised telomeres.Chromosoma. 2012 Jun;121(3):277-90. doi: 10.1007/s00412-011-0359-0. Chromosoma. 2012. PMID: 22289863 Free PMC article.
-
dNTP pools determine fork progression and origin usage under replication stress.EMBO J. 2012 Feb 15;31(4):883-94. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.470. Epub 2012 Jan 10. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22234185 Free PMC article.
-
Mdt1 facilitates efficient repair of blocked DNA double-strand breaks and recombinational maintenance of telomeres.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Sep;27(18):6532-45. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00471-07. Epub 2007 Jul 16. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17636027 Free PMC article.
-
Replisome function during replicative stress is modulated by histone h3 lysine 56 acetylation through Ctf4.Genetics. 2015 Apr;199(4):1047-63. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.173856. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 25697176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen, J. B., Z. Zhou., W. Siede., E. C. Friedberg, and S. J. Elledge. 1994. The SAD1/RAD53 protein kinase controls multiple checkpoints and DNA damage-induced transcription in yeast. Genes Dev. 8:2401-2415. - PubMed
-
- Bachant, J. B., and S. J. Elledge. 1999. Mitotic treasures in the nucleolus. Nature 398:757-768. - PubMed
-
- Bertuch, A., and V. Lundblad. 2003. Which end: dissecting Ku's function at telomeres and double-strand breaks. Genes Dev. 17:2347-2350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
