Critical interactions between TGF-beta signaling/ELF, and E-cadherin/beta-catenin mediated tumor suppression
- PMID: 16288220
- PMCID: PMC3821559
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209211
Critical interactions between TGF-beta signaling/ELF, and E-cadherin/beta-catenin mediated tumor suppression
Erratum in
-
Correction: critical interactions between TGF-β signaling/ELF, and E-cadherin/β-catenin mediated tumor suppression.Oncogene. 2021 May;40(18):3348-3349. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01632-1. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33875789 No abstract available.
Abstract
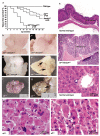
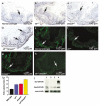
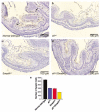
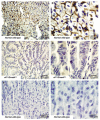
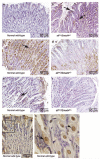
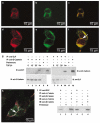
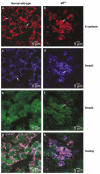
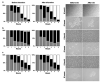
Inactivation of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) pathway occurs often in malignancies of the gastrointestinal (GI) system. However, only a fraction of sporadic GI tumors exhibit inactivating mutations in early stages of cancer formation, suggesting that other mechanisms play a critical role in the inactivation of this pathway. Here, we show a wide range of GI tumors, including those of the stomach, liver and colon in elf+/- and elf+/- / Smad4+/- mutant mice. We found that embryonic liver fodrin (ELF), a beta-Spectrin originally identified in endodermal stem/progenitor cells committed to foregut lineage, possesses potent antioncogenic activity and is frequently inactivated in GI cancers. Specifically, E-cadherin accumulation at cell-cell contacts and E-cadherin-beta-catenin-dependent epithelial cell-cell adhesion is disrupted in elf+/- / Smad4+/- mutant gastric epithelial cells, and could be rescued by ectopic expression of full-length elf, but not Smad3 or Smad4. Subcellular fractionation revealed that E-cadherin is expressed mainly at the cell membrane after TGF-beta stimulation. In contrast, elf+/- / Smad4+/- mutant tissues showed abnormal distribution of E-cadherin that could be rescued by overexpression of ELF but not Smad3 or Smad4. Our results identify a group of common lethal malignancies in which inactivation of TGF-beta signaling, which is essential for tumor suppression, is disrupted by inactivation of the ELF adaptor protein.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of PRAJA and ELF in TGF-beta signaling and gastric cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2005 Jul;4(7):694-9. doi: 10.4161/cbt.4.7.2015. Epub 2005 Jul 13. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005. PMID: 16096365 Review.
-
Inactivation of ELF/TGF-beta signaling in human gastrointestinal cancer.Oncogene. 2005 Dec 1;24(54):8012-24. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208946. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 16158060
-
Disruption of transforming growth factor-beta signaling in ELF beta-spectrin-deficient mice.Science. 2003 Jan 24;299(5606):574-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1075994. Science. 2003. PMID: 12543979
-
Transforming growth factor-beta suppresses nonmetastatic colon cancer through Smad4 and adaptor protein ELF at an early stage of tumorigenesis.Cancer Res. 2005 May 15;65(10):4228-37. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4585. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15899814
-
Molecular aspects of adhesion-epigenetic mechanisms for inactivation of the E-Cadherin-mediated cell adhesion system in cancers.Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 2000;84:28-32. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 2000. PMID: 11217445 Review.
Cited by
-
Progenitor/stem cells give rise to liver cancer due to aberrant TGF-beta and IL-6 signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Feb 19;105(7):2445-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705395105. Epub 2008 Feb 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18263735 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Mechanism of Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling for Intestinal Fibrosis: A Mini-Review.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 27;10:162. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00162. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30873033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Administration of Steamed and Freeze-Dried Mature Silkworm Larval Powder Prevents Hepatic Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinogenesis by Blocking TGF-β/STAT3 Signaling Cascades in Rats.Cells. 2020 Feb 28;9(3):568. doi: 10.3390/cells9030568. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32121064 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of TGF-β adaptor β2SP activates notch signaling and SOX9 expression in esophageal adenocarcinoma.Cancer Res. 2013 Apr 1;73(7):2159-69. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1962. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23536563 Free PMC article.
-
SPTBN1 suppresses the progression of epithelial ovarian cancer via SOCS3-mediated blockade of the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jun 8;12(11):10896-10911. doi: 10.18632/aging.103303. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32516133 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

