Overall obesity, abdominal adiposity, diabetes and cigarette smoking in relation to the risk of pancreatic cancer in two Swedish population-based cohorts
- PMID: 16288300
- PMCID: PMC2361517
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602868
Overall obesity, abdominal adiposity, diabetes and cigarette smoking in relation to the risk of pancreatic cancer in two Swedish population-based cohorts
Abstract
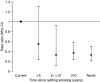
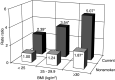
We examined the associations of body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, a history of diabetes, and cigarette smoking with risk of pancreatic cancer among 37,147 women and 45,906 men followed up during 560,666 person-years in the Swedish Mammography Cohort and the Cohort of Swedish Men; 136 incident cases of pancreatic cancer were diagnosed. The multivariate rate ratio (RR) of pancreatic cancer for obese women and men (BMI > or =30 kg/m(2)) was 1.81 (95% CI: 1.04-3.15) compared to those with a BMI of 20-25 kg/m(2). For a difference of 20 cm (about two standard deviations) in waist circumference, the multivariate RRs were 1.32 (95% CI: 0.73-2.37) among women and 1.74 (95% CI: 1.00-3.01) among men. Pancreatic cancer risk was associated with history of diabetes (multivariate RR: 1.88; 95% CI: 1.09-3.26) and cigarette smoking (multivariate RR for current compared with never smokers: 3.06; 95% CI: 1.99-4.72). Current smokers of > or =40 pack-years had a five-fold elevated risk compared with never smokers. Risk among past smokers approached the RR for never smokers within 5-10 years following smoking cessation. Findings from this prospective study support positive relationships of overall obesity, abdominal adiposity, diabetes and smoking with risk of pancreatic cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Bergmann U, Funatomi H, Yokoyama M, Beger HG, Korc M (1995) Insulin-like growth factor I overexpression in human pancreatic cancer: evidence for autocrine and paracrine roles. Cancer Res 55: 2007–2011 - PubMed
-
- Boyle P, Ferlay J (2005) Cancer incidence and mortality in Europe, 2004. Ann Oncol 16: 481–488 - PubMed
-
- Cox DR, Oakes D (1984) Analysis of Survival Data. London: Chapman & Hall
-
- Fisher WE, Boros LG, Schirmer WJ (1996) Insulin promotes pancreatic cancer: evidence for endocrine influence on exocrine pancreatic tumors. J Surg Res 63: 310–313 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

