Interaction between HIF-1 alpha (ODD) and hARD1 does not induce acetylation and destabilization of HIF-1 alpha
- PMID: 16288748
- PMCID: PMC4505811
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.10.036
Interaction between HIF-1 alpha (ODD) and hARD1 does not induce acetylation and destabilization of HIF-1 alpha
Abstract
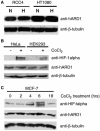
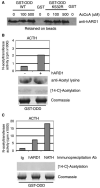
Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1 alpha) is a central component of the cellular responses to hypoxia. Hypoxic conditions result in stabilization of HIF-1 alpha and formation of the transcriptionally active HIF-1 complex. It was suggested that mammalian ARD1 acetylates HIF-1 alpha and thereby enhances HIF-1 alpha ubiquitination and degradation. Furthermore, ARD1 was proposed to be down-regulated in hypoxia thus facilitating the stabilization of HIF-1 alpha. Here we demonstrate that the level of human ARD1 (hARD1) protein is not decreased in hypoxia. Moreover, hARD1 does not acetylate and destabilize HIF-1 alpha. However, we find that hARD1 specifically binds HIF-1 alpha, suggesting a putative, still unclear, connection between these proteins.
Figures


References
-
- Marti HH. Angiogenesis – a self-adapting principle in hypoxia. EXS. 2005:163–180. - PubMed
-
- Acker T, Plate KH. Role of hypoxia in tumor angiogenesis-molecular and cellular angiogenic crosstalk. Cell Tissue Res. 2003;314:145–155. - PubMed
-
- Vaupel P. The role of hypoxia-induced factors in tumor progression. Oncologist. 2004;(Suppl. 5):10–17. - PubMed
-
- Bacon AL, Harris AL. Hypoxia-inducible factors and hypoxic cell death in tumour physiology. Ann. Med. 2004;36:530–539. - PubMed
-
- Metzen E, Ratcliffe PJ. HIF hydroxylation and cellular oxygen sensing. Biol. Chem. 2004;385:223–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

