A role for protein phosphatases 1, 2A, and 2B in cerebellar long-term potentiation
- PMID: 16291950
- PMCID: PMC6725852
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2876-05.2005
A role for protein phosphatases 1, 2A, and 2B in cerebellar long-term potentiation
Abstract
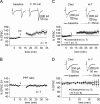
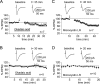
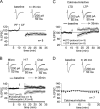
Cerebellar parallel fiber (PF)-Purkinje cell (PC) synapses can undergo postsynaptically expressed long-term depression (LTD) or long-term potentiation (LTP). PF-LTD induction requires the coactivity of the PF and CF (climbing fiber) inputs to PCs and a concomitant calcium transient and activation of protein kinase C (PKC). PF-LTP can be induced by PF activity alone and requires a lower calcium transient for its induction than PF-LTD. The cellular events triggering PF-LTP induction are not well characterized. At other types of synapses (e.g., in the hippocampus), bidirectional synaptic plasticity is under control of a kinase/phosphatase switch, with PKC and CaMKII (calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II) activity promoting LTP induction and phosphatase activity promoting LTD induction. Here, we have tested for the involvement of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1), PP2A, and PP2B (calcineurin) in cerebellar LTP induction using whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in rat cerebellar slices. LTP induction was blocked in the presence of the PP1/2A inhibitors okadaic acid and microcystin LR, the PP1 inhibitory peptide inhibitor-2, the PP2A inhibitor fostriecin, and the PP2B inhibitor cyclosporin A. LTP induction was not impaired by the PKC inhibitor chelerythrine. Conversely, LTD induction was not blocked by microcystin LR but instead was reduced when active PP2B was injected into PCs. These data indicate that a kinase/phosphatase switch controls bidirectional cerebellar plasticity, but in a manner "inverse" to the dependencies found at other types of synapses. Therefore, cerebellar LTP constitutes the only form of LTP described so far that depends on phosphatase rather than kinase activity.
Figures

References
-
- Ajima A, Ito M (1995) A unique role of protein phosphatases in cerebellar long-term depression. NeuroReport 6: 297-300. - PubMed
-
- Bear MF, Linden DJ (2000) The mechanisms and meaning of long-term synaptic depression in the mammalian brain. In: The synapse (Cowan WN, Südhof T, Stevens CF, eds), pp 455-517. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins UP.
-
- Blitzer RD, Connor JH, Brown GP, Wong T, Shenolikar S, Iyengar R, Landau EM (1998) Gating of CaMKII by cAMP-regulated protein phosphatase activity during LTP. Science 280: 1940-1943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
