Structure of the E. coli protein-conducting channel bound to a translating ribosome
- PMID: 16292303
- PMCID: PMC1351281
- DOI: 10.1038/nature04133
Structure of the E. coli protein-conducting channel bound to a translating ribosome
Abstract
Secreted and membrane proteins are translocated across or into cell membranes through a protein-conducting channel (PCC). Here we present a cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of the Escherichia coli PCC, SecYEG, complexed with the ribosome and a nascent chain containing a signal anchor. This reconstruction shows a messenger RNA, three transfer RNAs, the nascent chain, and detailed features of both a translocating PCC and a second, non-translocating PCC bound to mRNA hairpins. The translocating PCC forms connections with ribosomal RNA hairpins on two sides and ribosomal proteins at the back, leaving a frontal opening. Normal mode-based flexible fitting of the archaeal SecYEbeta structure into the PCC electron microscopy densities favours a front-to-front arrangement of two SecYEG complexes in the PCC, and supports channel formation by the opening of two linked SecY halves during polypeptide translocation. On the basis of our observation in the translocating PCC of two segregated pores with different degrees of access to bulk lipid, we propose a model for co-translational protein translocation.
Figures
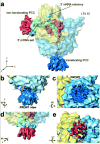
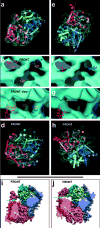
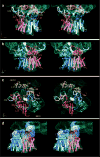

Comment in
-
Cell biology: two pores better than one?Nature. 2005 Nov 17;438(7066):299-300. doi: 10.1038/438299a. Nature. 2005. PMID: 16292298 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cryo-EM structure of the ribosome-SecYE complex in the membrane environment.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 May;18(5):614-21. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2026. Epub 2011 Apr 17. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21499241 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the SecY channel during initiation of protein translocation.Nature. 2014 Feb 6;506(7486):102-6. doi: 10.1038/nature12720. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24153188 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of the Sec61 complex engaged in nascent peptide translocation or membrane insertion.Nature. 2014 Feb 6;506(7486):107-10. doi: 10.1038/nature12950. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24499919
-
The structure of the bacterial protein translocation complex SecYEG.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Dec;33(Pt 6):1225-30. doi: 10.1042/BST0331225. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16246086 Review.
-
The machinery of membrane protein assembly.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004 Aug;14(4):397-404. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.07.003. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004. PMID: 15313232 Review.
Cited by
-
Competitive binding of the SecA ATPase and ribosomes to the SecYEG translocon.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 9;287(11):7885-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.297911. Epub 2012 Jan 20. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22267723 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of transmembrane helices in vivo--is hydrophobicity all that matters?J Gen Physiol. 2007 May;129(5):353-6. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200709740. Epub 2007 Apr 16. J Gen Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17438115 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Dealing with structural variability in molecular replacement and crystallographic refinement through normal-mode analysis.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2008 Jan;64(Pt 1):40-8. doi: 10.1107/S0907444907053516. Epub 2007 Dec 5. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2008. PMID: 18094466 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of GTPase activation at the signal recognition particle (SRP) RNA distal end.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 20;288(51):36385-97. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.513614. Epub 2013 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24151069 Free PMC article.
-
Collective dynamics of the ribosomal tunnel revealed by elastic network modeling.Proteins. 2009 Jun;75(4):837-45. doi: 10.1002/prot.22292. Proteins. 2009. PMID: 19004020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simon SM, Blobel G. A protein-conducting channel in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1991;65:371–380. - PubMed
-
- Wickner W, Driessen AJM, Hartl FU. The enzymology of protein translocation across the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:101–124. - PubMed
-
- Brundage L, et al. The purified E. coli integral membrane protein SecY/E is sufficient for reconstitution of SecA-dependent precursor protein translocation. Cell. 1990;62:649–657. - PubMed
-
- Gorlich D, Rapoport TA. Protein translocation into proteoliposomes reconstituted from purified components of the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Cell. 1993;75:615–30. - PubMed
-
- Gilmore R, Blobel G. Translocation of secretory proteins across the microsomal membrane occurs through an environment accessible to aqueous perturbants. Cell. 1985;42:497–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

