Structure of unliganded HSV gD reveals a mechanism for receptor-mediated activation of virus entry
- PMID: 16292345
- PMCID: PMC1356314
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600875
Structure of unliganded HSV gD reveals a mechanism for receptor-mediated activation of virus entry
Abstract
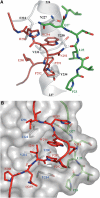
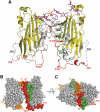
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) entry into cells requires binding of the envelope glycoprotein D (gD) to one of several cell surface receptors. The 50 C-terminal residues of the gD ectodomain are essential for virus entry, but not for receptor binding. We have determined the structure of an unliganded gD molecule that includes these C-terminal residues. The structure reveals that the C-terminus is anchored near the N-terminal region and masks receptor-binding sites. Locking the C-terminus in the position observed in the crystals by an intramolecular disulfide bond abolished receptor binding and virus entry, demonstrating that this region of gD moves upon receptor binding. Similarly, a point mutant that would destabilize the C-terminus structure was nonfunctional for entry, despite increased affinity for receptors. We propose that a controlled displacement of the gD C-terminus upon receptor binding is an essential feature of HSV entry, ensuring the timely activation of membrane fusion.
Figures




References
-
- Campadelli-Fiume G, Cocchi F, Menotti L, Lopez M (2000) The novel receptors that mediate the entry of herpes simplex viruses and animal alphaherpesviruses into cells. Rev Med Virol 10: 305–319 - PubMed
-
- Carfi A, Gong H, Lou H, Willis SH, Cohen GH, Eisenberg RJ, Wiley DC (2002) Crystallization and preliminary diffraction studies of the ectodomain of the envelope glycoprotein D from herpes simplex virus 1 alone and in complex with the ectodomain of the human receptor HveA. Acta Crystallogr D 58: 836–838 - PubMed
-
- Carfi A, Willis SH, Whitbeck JC, Krummenacher C, Cohen GH, Eisenberg RJ, Wiley DC (2001) Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D bound to the human receptor HveA. Mol Cell 8: 169–179 - PubMed
-
- CCP4 (1994) The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D 50: 760–763 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

