MINISEED3 (MINI3), a WRKY family gene, and HAIKU2 (IKU2), a leucine-rich repeat (LRR) KINASE gene, are regulators of seed size in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 16293693
- PMCID: PMC1297679
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508418102
MINISEED3 (MINI3), a WRKY family gene, and HAIKU2 (IKU2), a leucine-rich repeat (LRR) KINASE gene, are regulators of seed size in Arabidopsis
Abstract
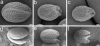
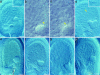
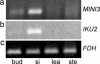
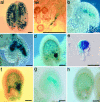
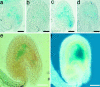
We have identified mutant alleles of two sporophytically acting genes, HAIKU2 (IKU2) and MINISEED3 (MINI3). Homozygotes of these alleles produce a small seed phenotype associated with reduced growth and early cellularization of the endosperm. This phenotype is similar to that described for another seed size gene, IKU1. MINI3 encodes WRKY10, a WRKY class transcription factor. MINI3 promoter::GUS fusions show the gene is expressed in pollen and in the developing endosperm from the two nuclei stage at approximately 12 hr postfertilization to endosperm cellularization at approximately 96 hr. MINI3 is also expressed in the globular embryo but not in the late heart stage of embryo development. The early endosperm expression of MINI3 is independent of its parent of origin. IKU2 encodes a leucine-rich repeat (LRR) KINASE (At3g19700). IKU2::GUS has a similar expression pattern to that of MINI3. The patterns of expression of the two genes and their similar phenotypes indicate they may operate in the same genetic pathway. Additionally, we found that both MINI3 and IKU2 showed decreased expression in the iku1-1 mutant. IKU2 expression was reduced in a mini3-1 background, whereas MINI3 expression was unaltered in the iku2-3 mutant. These data suggest the successive action of the three genes IKU1, IKU2, and MINI3 in the same pathway of seed development.
Figures

References
-
- Faure, J. E., Rotman, N., Fortuné, P. & Dumas, C. (2002) Plant J. 30, 481-488. - PubMed
-
- Olsen, O. A. (2001) Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 52, 233-267. - PubMed
-
- Sorensen, M. B., Mayer, U., Lukowitz, W., Robert, H., Chambrier, P., Jurgens, G., Somerville, C., Lepiniec, L. & Berger, F. (2002) Development (Cambridge, U.K.) 129, 5567-5576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

