Timp3 deficiency in insulin receptor-haploinsufficient mice promotes diabetes and vascular inflammation via increased TNF-alpha
- PMID: 16294222
- PMCID: PMC1283942
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI26052
Timp3 deficiency in insulin receptor-haploinsufficient mice promotes diabetes and vascular inflammation via increased TNF-alpha
Abstract
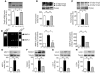
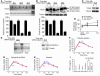
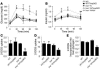
Activation of inflammatory pathways may contribute to the beginning and the progression of both atherosclerosis and type 2 diabetes. Here we report a novel interaction between insulin action and control of inflammation, resulting in glucose intolerance and vascular inflammation and amenable to therapeutic modulation. In insulin receptor heterozygous (Insr+/-) mice, we identified the deficiency of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 (Timp3, an inhibitor of both TNF-alpha-converting enzyme [TACE] and MMPs) as a common bond between glucose intolerance and vascular inflammation. Among Insr+/- mice, those that develop diabetes have reduced Timp3 and increased TACE activity. Unchecked TACE activity causes an increase in levels of soluble TNF-alpha, which subsequently promotes diabetes and vascular inflammation. Double heterozygous Insr+/-Timp3+/- mice develop mild hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia at 3 months and overt glucose intolerance and hyperinsulinemia at 6 months. A therapeutic role for Timp3/TACE modulation is supported by the observation that pharmacological inhibition of TACE led to marked reduction of hyperglycemia and vascular inflammation in Insr+/- diabetic mice, as well as by the observation of increased insulin sensitivity in Tace+/- mice compared with WT mice. Our results suggest that an interplay between reduced insulin action and unchecked TACE activity promotes diabetes and vascular inflammation.
Figures


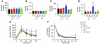

References
-
- Warram JH, Martin BC, Krolewski AS, Soeldner JS, Kahn CR. Slow glucose removal rate and hyperinsulinemia precede the development of type II diabetes in the offspring of diabetic parents. Ann. Intern. Med. 1990;113:909–915. - PubMed
-
- Rewers M, et al. Insulin sensitivity, insulinemia, and coronary artery disease: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:781–787. - PubMed
-
- Stern MP. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The “common soil” hypothesis. Diabetes. 1995;44:369–374. - PubMed
-
- Festa A, et al. Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of the insulin resistance syndrome: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS) Circulation. 2000;102:42–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

