Identification of thrombospondin 1 (TSP-1) as a novel mediator of cell injury in kidney ischemia
- PMID: 16294224
- PMCID: PMC1283940
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI25461
Identification of thrombospondin 1 (TSP-1) as a novel mediator of cell injury in kidney ischemia
Erratum in
- J Clin Invest. 2006 Feb;116(2):549
Abstract
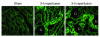
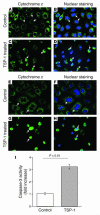
Thrombospondin 1 (TSP-1) is a matricellular protein that inhibits angiogenesis and causes apoptosis in vivo and in vitro in several cancerous cells and tissues. Here we identify TSP-1 as the molecule with the highest induction level at 3 hours of IR injury in rat and mouse kidneys subjected to ischemia/reperfusion (IR) injury using the DNA microarray approach. Northern hybridizations demonstrated that TSP-1 expression was undetectable at baseline, induced at 3 and 12 hours, and returned to baseline levels at 48 hours of reperfusion. Immunocytochemical staining identified the injured proximal tubules as the predominant sites of expression of TSP-1 in IR injury and showed colocalization of TSP-1 with activated caspase-3. Addition of purified TSP-1 to normal kidney proximal tubule cells or cells subjected to ATP depletion in vitro induced injury as demonstrated by cytochrome c immunocytochemical staining and caspase-3 activity. The deleterious role of TSP-1 in ischemic kidney injury was demonstrated directly in TSP-1 null mice, which showed significant protection against IR injury-induced renal failure and tubular damage. We propose that TSP-1 is a novel regulator of ischemic damage in the kidney and may play an important role in the pathophysiology of ischemic kidney failure.
Figures

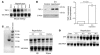


References
-
- Bonventre JV. Mechanisms of ischemic acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 1993;43:1160–1178. - PubMed
-
- Tritto I, et al. A short burst of oxygen radicals at reflow induces sustained release of oxidized glutathione from postischemic hearts. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998;24:290–297. - PubMed
-
- Sutton TA, Molitoris BA. Mechanisms of cellular injury in ischemic acute renal failure. Semin. Nephrol. 1998;18:490–497. - PubMed
-
- Rabb H, Wang Z, Postler G, Soleimani M. Possible molecular basis for changes in potassium handling in acute renal failure. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000;35:871–877. - PubMed
-
- Sheridan AM, Bonventre JV. Cell biology and molecular mechanisms of injury in ischemic acute renal failure. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2000;9:427–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

