Phosphorylation of the VP16 transcriptional activator protein during herpes simplex virus infection and mutational analysis of putative phosphorylation sites
- PMID: 16297954
- PMCID: PMC1717022
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.10.011
Phosphorylation of the VP16 transcriptional activator protein during herpes simplex virus infection and mutational analysis of putative phosphorylation sites
Abstract
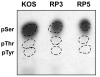
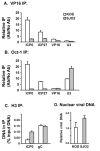
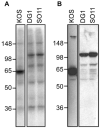
VP16 is a virion phosphoprotein of herpes simplex virus and a transcriptional activator of the viral immediate-early (IE) genes. We identified four novel VP16 phosphorylation sites (Ser18, Ser353, Ser411, and Ser452) at late times in infection but found no evidence of phosphorylation of Ser375, a residue reportedly phosphorylated when VP16 is expressed from a transfected plasmid. A virus carrying a Ser375Ala mutation of VP16 was viable in cell culture but with a slow growth rate. The association of the mutant VP16 protein with IE gene promoters and subsequent IE gene expression was markedly reduced during infection, consistent with prior transfection and in vitro results. Surprisingly, the association of Oct-1 with IE promoters was also diminished during infection by the mutant strain. We propose that Ser375 is important for the interaction of VP16 with Oct-1, and that the interaction is required to enable both proteins to bind to IE promoters.
Figures






References
-
- Berger SL, Pina B, Silverman N, Marcus GA, Agapite J, Regier JL, Triezenberg SJ, Guarente L. Genetic isolation of ADA2 - a potential transcriptional adaptor required for function of certain acidic activation domains. Cell. 1992;70:251–265. - PubMed
-
- Cress A, Triezenberg SJ. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the gene encoding virion protein 16 of herpes simplex virus type 2. Gene. 1991a;103:235–8. - PubMed
-
- Cress WD, Triezenberg SJ. Critical structural elements of the VP16 transcriptional activation domain. Science. 1991b;251:87–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

