Experience induces structural and biochemical changes in the adult primate brain
- PMID: 16299105
- PMCID: PMC1297690
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508817102
Experience induces structural and biochemical changes in the adult primate brain
Abstract
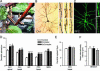
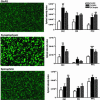
Primates exhibit complex social and cognitive behavior in the wild. In the laboratory, however, the expression of their behavior is usually limited. A large body of literature shows that living in an enriched environment alters dendrites and synapses in the brains of adult rodents. To date, no studies have investigated the influence of living in a complex environment on brain structure in adult primates. We assessed dendritic architecture, dendritic spines, and synaptic proteins in adult marmosets housed in either a standard laboratory cage or in one of two differentially complex habitats. A month-long stay in either complex environment enhanced the length and complexity of the dendritic tree and increased dendritic spine density and synaptic protein levels in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. No differences were detected between the brains of marmosets living in the two differentially complex environments. Our results show that the structure of the adult primate brain remains highly sensitive even to modest levels of experiential complexity. For adult primates, living in standard laboratory housing may induce reversible dendritic spine and synapse decreases in brain regions important for cognition.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fragile X mental retardation protein levels increase following complex environment exposure in rat brain regions undergoing active synaptogenesis.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2005 May;83(3):180-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2004.11.004. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2005. PMID: 15820853
-
Developmental expression profiles of axon guidance signaling and the immune system in the marmoset cortex: potential molecular mechanisms of pruning of dendritic spines during primate synapse formation in late infancy and prepuberty (I).Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Feb 14;444(3):302-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.024. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24485715
-
Pathway specificity of dendritic spine morphology in identified synapses onto rat hippocampal CA1 neurons in organotypic slices.Hippocampus. 2006;16(12):1111-24. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20236. Hippocampus. 2006. PMID: 17068782
-
Amyloid beta: a putative intra-spinal microtubule-depolymerizer to induce synapse-loss or dentritic spine shortening in Alzheimer's disease.Ital J Anat Embryol. 2009 Apr-Sep;114(2-3):109-20. Ital J Anat Embryol. 2009. PMID: 20198823 Review.
-
Dendritic spine plasticity: looking beyond development.Brain Res. 2007 Dec 12;1184:65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.02.094. Epub 2006 Apr 5. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 16600191 Review.
Cited by
-
Melanocortin-4 receptor regulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity through a protein kinase A-dependent mechanism.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 9;33(2):464-72. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3282-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23303927 Free PMC article.
-
Resilience to the effects of social stress on vulnerability to developing drug addiction.World J Psychiatry. 2022 Jan 19;12(1):24-58. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i1.24. eCollection 2022 Jan 19. World J Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35111578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV mediates distinct features of basal and activity-dependent dendrite complexity.Neuroscience. 2011 Dec 29;199:548-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.09.048. Epub 2011 Oct 1. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21989476 Free PMC article.
-
Physical exercise enhances cognitive flexibility as well as astrocytic and synaptic markers in the medial prefrontal cortex.PLoS One. 2015 May 4;10(5):e0124859. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124859. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25938418 Free PMC article.
-
Enriching Communicative Environments: Leveraging Advances in Neuroplasticity for Improving Outcomes in Neurogenic Communication Disorders.Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2019 Mar 11;28(1S):216-229. doi: 10.1044/2018_AJSLP-17-0157. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30453323 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rosenzweig, M. R., Krech, D., Bennett, E. L. & Diamond, M. C. (1962) J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 55, 429-437. - PubMed
-
- Walsh, R. N. (1980) Int. J. Neurosci. 11, 77-89. - PubMed
-
- Renner, M. & Rosenzweig, M. (1987) Enriched and Impoverished Environments (Springer, New York).
-
- Diamond, M. C. (1988) Enriching Heredity: The Impact of the Environment on the Anatomy of the Brain (Collier Macmillan, New York).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

