Inhibition of target of rapamycin signaling by rapamycin in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- PMID: 16299168
- PMCID: PMC1310555
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.105.070847
Inhibition of target of rapamycin signaling by rapamycin in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Abstract
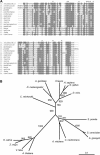
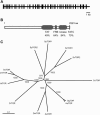
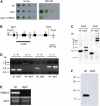
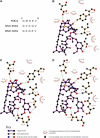
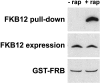
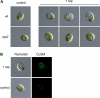
The macrolide rapamycin specifically binds the 12-kD FK506-binding protein (FKBP12), and this complex potently inhibits the target of rapamycin (TOR) kinase. The identification of TOR in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) revealed that TOR is conserved in photosynthetic eukaryotes. However, research on TOR signaling in plants has been hampered by the natural resistance of plants to rapamycin. Here, we report TOR inactivation by rapamycin treatment in a photosynthetic organism. We identified and characterized TOR and FKBP12 homologs in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Whereas growth of wild-type Chlamydomonas cells is sensitive to rapamycin, cells lacking FKBP12 are fully resistant to the drug, indicating that this protein mediates rapamycin action to inhibit cell growth. Unlike its plant homolog, Chlamydomonas FKBP12 exhibits high affinity to rapamycin in vivo, which was increased by mutation of conserved residues in the drug-binding pocket. Furthermore, pull-down assays demonstrated that TOR binds FKBP12 in the presence of rapamycin. Finally, rapamycin treatment resulted in a pronounced increase of vacuole size that resembled autophagic-like processes. Thus, our findings suggest that Chlamydomonas cell growth is positively controlled by a conserved TOR kinase and establish this unicellular alga as a useful model system for studying TOR signaling in photosynthetic eukaryotes.
Figures

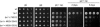

References
-
- Beck T, Hall MN (1999) The TOR signalling pathway controls nuclear localization of nutrient-regulated transcription factors. Nature 402: 689–692 - PubMed
-
- Bjornsti MA, Houghton PJ (2004) The TOR pathway: a target for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 335–348 - PubMed
-
- Brillantes AB, Ondrias K, Scott A, Kobrinsky E, Ondriasova E, Moschella MC, Jayaraman T, Landers M, Ehrlich BE, Marks AR (1994) Stabilization of calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) function by FK506-binding protein. Cell 77: 513–523 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

