Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin damages the human intestine in vitro
- PMID: 16299340
- PMCID: PMC1307077
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.12.8407-8410.2005
Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin damages the human intestine in vitro
Abstract
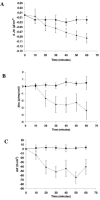
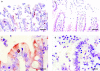
In vitro, Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin (CPE) binds to human ileal epithelium and induces morphological damage concurrently with reduced short-circuit current, transepithelial resistance, and net water absorption. CPE also binds to the human colon in vitro but causes only slight morphological and transport changes that are not statistically significant.
Figures

References
-
- Bos, J., L. Smithee, B. A. McClane, R. F. Distefano, F. A. Uzal, G. Songer, S. Mallonee, and, J. M. Crutcher. 2005. Fatal necrotizing colitis following a foodborne outbreak of enterotoxigenic Clostridium perfringens type A infection. J. Clin. Infect. Dis. 40:e78-e83. - PubMed
-
- Dorr, R. A., A. Kierbel, J. Vera, and M. Parisi. 1997. A new data-acquisition system for the measurement of the net water flux across epithelia. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 53:9-14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

