Mutant mitochondrial helicase Twinkle causes multiple mtDNA deletions and a late-onset mitochondrial disease in mice
- PMID: 16301523
- PMCID: PMC1308896
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0505551102
Mutant mitochondrial helicase Twinkle causes multiple mtDNA deletions and a late-onset mitochondrial disease in mice
Abstract
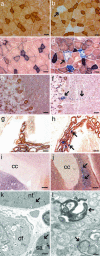
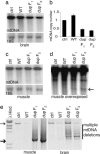
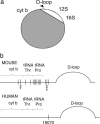
Defects of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) maintenance have recently been associated with inherited neurodegenerative and muscle diseases and the aging process. Twinkle is a nuclear-encoded mtDNA helicase, dominant mutations of which cause adult-onset progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO) with multiple mtDNA deletions. We have generated transgenic mice expressing mouse Twinkle with PEO patient mutations. Multiple mtDNA deletions accumulate in the tissues of these mice, resulting in progressive respiratory dysfunction and chronic late-onset mitochondrial disease starting at 1 year of age. The muscles of the mice faithfully replicate all of the key histological, genetic, and biochemical features of PEO patients. Furthermore, the mice have progressive deficiency of cytochrome c oxidase in distinct neuronal populations. These "deletor" mice do not, however, show premature aging, indicating that subtle accumulation of mtDNA deletions and progressive respiratory chain dysfunction are not sufficient to accelerate aging. This model is a valuable tool for therapy development and testing for adult-onset mitochondrial disorders.
Figures
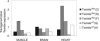
References
-
- Zeviani, M., Servidei, S., Gellera, C., Bertini, E., DiMauro, S. & DiDonato, S. (1989) Nature 339, 309–311. - PubMed
-
- Van Goethem, G., Dermaut, B., Lofgren, A., Martin, J. J. & Van Broeckhoven, C. (2001) Nat. Genet. 28, 211–212. - PubMed
-
- Van Goethem, G., Luoma, P., Rantamaki, M., Al Memar, A., Kaakkola, S., Hackman, P., Krahe, R., Lofgren, A., Martin, J. J., De Jonghe, P., et al. (2004) Neurology 63, 1251–1257. - PubMed
-
- Luoma, P., Melberg, A., Rinne, J. O., Kaukonen, J. A., Nupponen, N. N., Chalmers, R. M., Oldfors, A., Rautakorpi, I., Peltonen, L., Majamaa, K. et al. (2004) Lancet 364, 875–882. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

