Effects of MAP kinase inhibitors on epidermal growth factor-induced neoplastic transformation of human keratinocytes
- PMID: 16302268
- PMCID: PMC2227316
- DOI: 10.1002/mc.20160
Effects of MAP kinase inhibitors on epidermal growth factor-induced neoplastic transformation of human keratinocytes
Abstract
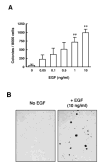
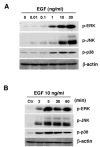
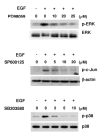
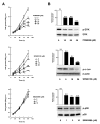
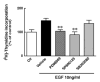
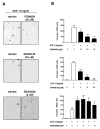
We previously reported data regarding the mechanism of neoplastic transformation in JB6 Cl41 mouse skin epidermal cells. However, experimental in vitro models for studying neoplastic transformation of human cells could provide further insight into the mechanisms of human cancer development. In this study, we have established a neoplastic transformation model with HaCaT cells, a human keratinocyte cell line, and showed the usefulness of this cell line for studying the mechanisms of neoplastic transformation. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) treatment induced a dose-dependent anchorage-independent cell transformation in HaCaT cells. Furthermore, PD98059, a mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/ERK kinase (MEK) inhibitor, or SP600125, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor, decreased cell growth, EGF-induced DNA synthesis and transformation. Unlike observations in the JB6 mouse epidermal cell model, SB203580, a stress-activated protein kinase-2/p38 alpha and beta (p38) inhibitor, increased EGF-induced transformation in HaCaT cells. These results suggest that extracellular-signal regulated kinase (ERK), JNK, or p38 are implicated in EGF-induced neoplastic transformation of human cells.
2005 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Lage A, Crombet T, Gonzalez G. Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor signaling: early results and future trends in oncology. Ann Med. 2003;35(5):327–336. - PubMed
-
- Dong Z, Huang C, Ma WY. PI-3 kinase in signal transduction, cell transformation, and as a target for chemoprevention of cancer. Anticancer Res. 1999;19(5A):3743–3747. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

