Activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) by connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) is involved in sustaining the survival of primary rat hepatic stellate cells
- PMID: 16303051
- PMCID: PMC1308830
- DOI: 10.1186/1478-811X-3-14
Activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) by connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) is involved in sustaining the survival of primary rat hepatic stellate cells
Abstract
Background/aims: Connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) is a matricellular protein that plays a role in hepatic stellate cell (HSC)-mediated fibrogenesis. The aim of this study was to investigate the regulation by CCN2 of cell survival pathways in primary HSC.
Methods: Primary HSC were obtained by in situ enzymatic perfusion of rat liver. NF-kappaB activation was assessed by immunoblotting for IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and degradation and by NF-kappaB p50 or p65 nuclear accumulation. NF-kappaB DNA-binding activity was determined by gel mobility shift assay while NF-kappaB response gene expression was evaluated using a luciferase reporter. Cell viability was assessed by Trypan blue staining or ATP luminescent assay while apoptosis was evaluated by caspase-3 activity.
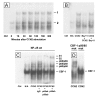
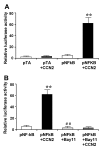
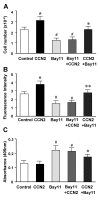
Results: CCN2 induced IkappaBalpha phosphorylation and degradation as well as nuclear accumulation of NF-kappaB. Activated NF-kappaB comprised three dimers, p65/p65, p65/p50 and p50/p50, that individually bound to DNA-binding sites and subsequently triggered transcriptional activity. This was confirmed by showing that CCN2 promoted activity of a NF-kappaB luciferase reporter. CCN2 promoted survival of serum-starved HSC and protected the cells from death induced by blocking the NF-kappaB signaling pathway using Bay-11-7082, a specific inhibitor of IkappaBalpha phosphorylation.
Conclusion: CCN2 contributes to the survival of primary HSC through the NF-kappaB pathway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Persistent activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in cultured rat hepatic stellate cells involves the induction of potentially novel Rel-like factors and prolonged changes in the expression of IkappaB family proteins.Hepatology. 1999 Sep;30(3):761-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300327. Hepatology. 1999. PMID: 10462383
-
Antioxidants attenuate reperfusion injury after global brain ischemia through inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B activity in rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2003 Nov;24(11):1125-30. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2003. PMID: 14627497
-
[Effects of different nuclear factor kappaB dimers on the survival of immortalized neural progenitor cells].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Apr 1;88(13):871-5. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18756949 Chinese.
-
Involvement of p65 in the regulation of NF-kappaB in rat hepatic stellate cells during cirrhosis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Jul 5;273(2):546-50. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.2993. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. PMID: 10873642
-
Upregulation of microRNA-126 in hepatic stellate cells may affect pathogenesis of liver fibrosis through the NF-κB pathway.DNA Cell Biol. 2015 Jul;34(7):470-80. doi: 10.1089/dna.2014.2760. Epub 2015 May 14. DNA Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25974152
Cited by
-
CCN2/CTGF is required for matrix organization and to protect growth plate chondrocytes from cellular stress.J Cell Commun Signal. 2013 Aug;7(3):219-30. doi: 10.1007/s12079-013-0201-y. Epub 2013 May 13. J Cell Commun Signal. 2013. PMID: 23666466 Free PMC article.
-
MRCK as a Potential Target for Claudin-Low Subtype of Breast Cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jan 1;20(1):1-14. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.88285. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38164185 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of CTGF in Inflammatory Responses Induced by Silica Particles in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells.Lung. 2019 Dec;197(6):783-791. doi: 10.1007/s00408-019-00272-x. Epub 2019 Sep 13. Lung. 2019. PMID: 31520180
-
Integrin expression and function in the response of primary culture hepatic stellate cells to connective tissue growth factor (CCN2).J Cell Mol Med. 2011 May;15(5):1087-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01072.x. Epub 2010 Apr 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 20406330 Free PMC article.
-
Connective tissue growth factor, a regulator related with 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid down-regulate MMPs in rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2012 Sep;32(9):2791-9. doi: 10.1007/s00296-011-1960-5. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Rheumatol Int. 2012. PMID: 21850473
References
-
- Gressner AM, Bachem MG. Cellular communications and cell-matrix interactions in the pathogenesis of fibroproliferative diseases: liver fibrosis as a paradigm. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1994;52:205–226. - PubMed
-
- Eng FJ, Friedman SL. Fibrogenesis I. New insights into hepatic stellate cell activation: the simple becomes complex. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2000;279:G7–G11. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

