Replication-independent histone deposition by the HIR complex and Asf1
- PMID: 16303565
- PMCID: PMC2819815
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.10.053
Replication-independent histone deposition by the HIR complex and Asf1
Abstract
The orderly deposition of histones onto DNA is mediated by conserved assembly complexes, including chromatin assembly factor-1 (CAF-1) and the Hir proteins . CAF-1 and the Hir proteins operate in distinct but functionally overlapping histone deposition pathways in vivo . The Hir proteins and CAF-1 share a common partner, the highly conserved histone H3/H4 binding protein Asf1, which binds the middle subunit of CAF-1 as well as to Hir proteins . Asf1 binds to newly synthesized histones H3/H4 , and this complex stimulates histone deposition by CAF-1 . In yeast, Asf1 is required for the contribution of the Hir proteins to gene silencing . Here, we demonstrate that Hir1, Hir2, Hir3, and Hpc2 comprise the HIR complex, which copurifies with the histone deposition protein Asf1. Together, the HIR complex and Asf1 deposit histones onto DNA in a replication-independent manner. Histone deposition by the HIR complex and Asf1 is impaired by a mutation in Asf1 that inhibits HIR binding. These data indicate that the HIR complex and Asf1 proteins function together as a conserved eukaryotic pathway for histone replacement throughout the cell cycle.
Figures

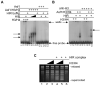


References
-
- Lamour V, Lecluse Y, Desmaze C, Spector M, Bodescot M, Aurias A, Osley MA, Lipinski M. A human homolog of the S. cerevisiae HIR1 and HIR2 transcriptional repressors cloned from the DiGeorge syndrome critical region. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1995;4:791–799. - PubMed
-
- Franco AA, Kaufman PD. Histone deposition proteins: links between the DNA replication machinery and epigenetic gene silencing. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. 2004;69:1–8. doi:10.1101/sqb.2004.1169.1017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

