The heterogeneous murine corneal stromal cell populations in vitro
- PMID: 16303944
- PMCID: PMC1610590
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.05-0117
The heterogeneous murine corneal stromal cell populations in vitro
Abstract
Purpose: To demonstrate that the murine corneal stroma is inhabited by heterogeneous cell populations that include cells expressing nestin.
Methods: Collagenase-isolated corneal stroma cells obtained from newborn and adult mice (2nd and 12th postnatal weeks, respectively), were seeded at low (5 cells/mm2), intermediate (50 cells/mm2), and high (500 cells/mm2) densities in DMEM/F12 containing insulin, transferrin, selenium, and 1% nonessential amino acids. Corneal stroma cells cultured at 500 cells/mm2 were treated with 10 ng/mL human recombinant transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 for 5 days. Cell morphology and expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin, choline acetyltransferase, CD45, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), keratocan, nestin, neurofilaments, protein gene product 9.5, tyrosine hydroxylase, and vimentin were examined.
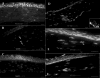
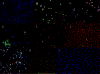
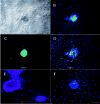
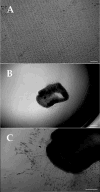
Results: Phase-contrast microscopy demonstrated that freshly isolated corneal stromal cells are heterogeneous in morphology and include dendritic, stellate, neuronal, and small polyhedral cells. Immunostaining of primary cultures of 2- and 12-week-old mice, 24 hours after seeding at the intermediate density, showed that 100% of cells expressed vimentin and 97.7% +/- 2.7% expressed keratocan. alpha-Smooth muscle actin was expressed by 0.2% +/- 0.05% of cells in the 2-week-old group and 0.1% +/- 0.07% in 12-week-old group. Neurofilament was expressed by 0.5% +/- 0.03% and 0.7% +/- 0.03% of cells in the 2- and 12-week-old groups, respectively. No cell expressed GFAP or nestin. After 5 days in culture, cells seeded at high density aggregated as clusters that were immunoreactive to nestin in both groups. Cell clusters and migrating cells reacted to pgp 9.5, and migrating cells, but not the cell clusters, reacted to tyrosine hydroxylase. Cell cluster formation and nestin expression were abolished by culturing in the presence of TGF-beta1.
Conclusions: Normal murine corneal stroma contains heterogeneous cell populations including cells with the potential to form clusters and express the progenitor marker nestin. This potential is disrupted by the addition of TGF-beta1 to the culture medium.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Sphere formation and expression of neural proteins by human corneal stromal cells in vitro.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 May;46(5):1620-5. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0288. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15851560
-
Class VI intermediate filament protein nestin is induced during activation of rat hepatic stellate cells.Hepatology. 1999 Feb;29(2):520-7. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290232. Hepatology. 1999. PMID: 9918930
-
Class III beta-tubulin is constitutively coexpressed with glial fibrillary acidic protein and nestin in midgestational human fetal astrocytes: implications for phenotypic identity.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008 Apr;67(4):341-54. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e31816a686d. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18379434
-
Long-lasting coexpression of nestin and glial fibrillary acidic protein in primary cultures of astroglial cells with a major participation of nestin(+)/GFAP(-) cells in cell proliferation.J Neurosci Res. 2006 Jun;83(8):1515-24. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20846. J Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16612832
-
Cerebellar gliomatosis in a toddler: case report of a challenging condition and review of the literature.J Child Neurol. 2012 Apr;27(4):511-20. doi: 10.1177/0883073811419315. Epub 2011 Sep 21. J Child Neurol. 2012. PMID: 21940698 Review.
Cited by
-
Genipin increases extracellular matrix synthesis preventing corneal perforation.Ocul Surf. 2023 Apr;28:115-123. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2023.02.003. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Ocul Surf. 2023. PMID: 36871831 Free PMC article.
-
Keratocyte-Derived Myofibroblasts: Functional Differences With Their Fibroblast Precursors.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Oct 3;64(13):9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.13.9. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 37796488 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained activation of ERK1/2 MAPK in Schwann cells causes corneal neurofibroma.J Neurosci Res. 2017 Sep;95(9):1712-1729. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24067. Epub 2017 May 10. J Neurosci Res. 2017. PMID: 28489286 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic models for investigating the nervous system: Currently available neurofluorescent reporters and potential neuronal markers.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020 Jul;1864(7):129595. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129595. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020. PMID: 32173376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors blocked activation and caused senescence of corneal stromal cells.Mol Vis. 2008;14:2556-65. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 19122829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chambers D, McGonnell IM. Neural crest: facing the facts of head development. Trends Genet. 2002;18:381–384. - PubMed
-
- Helms JA, Schneider RA. Cranial skeletal biology. Nature. 2003;423:326–331. - PubMed
-
- Noden DM. The control of avian cephalic neural crest cytodifferentiation. I. Skeletal and connective tissues. Dev Biol. 1978;67:296–312. - PubMed
-
- Johnston MC, Noden DM, Hazelton RD, et al. Origins of avian ocular and periocular tissues. Exp Eye Res. 1979;29:27–43. - PubMed
-
- Birk DE, Lande MA, Fernandez-Madrid FR. Collagen and glycosaminoglycan synthesis in aging human keratocyte cultures. Exp Eye Res. 1981;32:331–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

