IL-2 administration increases CD4+ CD25(hi) Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in cancer patients
- PMID: 16304057
- PMCID: PMC1473973
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-06-2399
IL-2 administration increases CD4+ CD25(hi) Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in cancer patients
Abstract
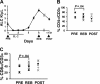
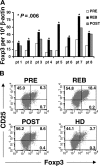
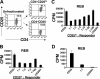
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is historically known as a T-cell growth factor. Accumulating evidence from knockout mice suggests that IL-2 is crucial for the homeostasis and function of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in vivo. However, the impact of administered IL-2 in an immune intact host has not been studied in rodents or humans. Here, we studied the impact of IL-2 administration on the frequency and function of human CD4+ CD25(hi) T cells in immune intact patients with melanoma or renal cancer. We found that the frequency of CD4+ CD25(hi) T cells was significantly increased after IL-2 treatment, and these cells expressed phenotypic markers associated with regulatory T cells. In addition, both transcript and protein levels of Foxp3, a transcription factor exclusively expressed on regulatory T cells, were consistently increased in CD4 T cells following IL-2 treatment. Functional analysis of the increased number of CD4+ CD25(hi) T cells revealed that this population exhibited potent suppressive activity in vitro. Collectively, our results demonstrate that administration of high-dose IL-2 increased the frequency of circulating CD4+ CD25(hi) Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Our findings suggest that selective inhibition of IL-2-mediated enhancement of regulatory T cells may improve the therapeutic effectiveness of IL-2 administration.
Figures


References
-
- Morgan DA, Ruscetti FW, Gallo R. Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows. Science. 1976;193: 1007-1008. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Topalian SL, et al. Treatment of 283 consecutive patients with metastatic melanoma or renal cell cancer using high-dose bolus interleukin 2. J Am Med Assoc. 1994;271: 907-913. - PubMed
-
- Malek TR, Bayer AL. Tolerance, not immunity, crucially depends on IL-2. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4: 665-674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

