Activities of acyclic nucleoside phosphonates against Orf virus in human and ovine cell monolayers and organotypic ovine raft cultures
- PMID: 16304144
- PMCID: PMC1315923
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.12.4843-4852.2005
Activities of acyclic nucleoside phosphonates against Orf virus in human and ovine cell monolayers and organotypic ovine raft cultures
Abstract
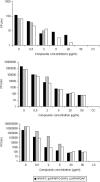
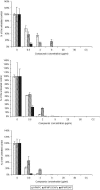
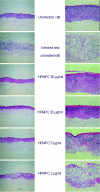
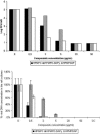
Orf virus, a member of the Parapoxvirus genus, causes a contagious pustular dermatitis in sheep, goats, and humans. Previous studies have demonstrated the activity of (S)-1-[3-hydroxy-2-(phosphonomethoxy)propyl]cytosine (HPMPC; cidofovir; Vistide) against orf virus in cell culture and humans. We have evaluated a broad range of acyclic nucleoside phosphonates (ANPs) against several orf virus strains in primary lamb keratinocytes (PLKs) and human embryonic lung (HEL) monolayers. HPMPC, (S)-9-[3-hydroxy-2-(phosphonomethoxy)propyl]-2,6- diaminopurine (HPMPDAP), and (R)-9-[3-hydroxy-2-(phosphonomethoxy)propoxy]-2,4-diaminopyrimidine (HPMPO-DAPy) were three of the most active compounds that were subsequently tested in a virus yield assay with PLK and HEL cells by virus titration and DNA quantification. HPMPC, HPMPDAP, and HPMPO-DAPy were evaluated for their activities against orf virus replication in organotypic epithelial raft cultures from differentiated PLK cells. At the highest concentrations (50 and 20 microg/ml), full protection was provided by the three drugs, while at 5 microg/ml, only HPMPDAP and HPMPC offered partial protection. The activities of the three compounds in the raft culture system were confirmed by quantification of infectious virus and viral DNA. These findings provide a rationale for the use of HPMPC and other ANPs in the treatment of orf (contagious ecthyma) in humans and animals.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vitro evaluation of the anti-orf virus activity of alkoxyalkyl esters of CDV, cCDV and (S)-HPMPA.Antiviral Res. 2007 Jul;75(1):52-7. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2006.11.010. Epub 2006 Dec 13. Antiviral Res. 2007. PMID: 17184854
-
Activities of several classes of acyclic nucleoside phosphonates against camelpox virus replication in different cell culture models.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Dec;51(12):4410-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00838-07. Epub 2007 Sep 24. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17893157 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral potential of a new generation of acyclic nucleoside phosphonates, the 6-[2-(phosphonomethoxy)alkoxy]-2,4-diaminopyrimidines.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2005;24(5-7):331-41. doi: 10.1081/ncn-200059772. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2005. PMID: 16247948
-
Therapeutic potential of nucleoside/nucleotide analogues against poxvirus infections.Rev Med Virol. 2004 Sep-Oct;14(5):289-300. doi: 10.1002/rmv.439. Rev Med Virol. 2004. PMID: 15334537 Review.
-
Acyclic nucleoside phosphonates in the chemotherapy of DNA virus and retrovirus infections.Intervirology. 1997;40(5-6):295-303. doi: 10.1159/000150563. Intervirology. 1997. PMID: 9675635 Review.
Cited by
-
Poxviruses Bearing DNA Polymerase Mutations Show Complex Patterns of Cross-Resistance.Biomedicines. 2022 Mar 1;10(3):580. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030580. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35327382 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of antiviral drug resistance of vaccinia virus: identification of residues in the viral DNA polymerase conferring differential resistance to antipoxvirus drugs.J Virol. 2008 Dec;82(24):12520-34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01528-08. Epub 2008 Oct 8. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18842735 Free PMC article.
-
Transdermal delivery and cutaneous targeting of antivirals using a penetration enhancer and lysolipid prodrugs.Pharm Res. 2014 Apr;31(4):1071-81. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-1228-8. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 24271238
-
Status Presens of Antiviral Drugs And Strategies: Part I: DNA Viruses and Retroviruses.Adv Antivir Drug Des. 2007;5:1-58. doi: 10.1016/S1075-8593(06)05001-5. Epub 2007 Sep 2. Adv Antivir Drug Des. 2007. PMID: 32288472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cidofovir Activity against Poxvirus Infections.Viruses. 2010 Dec;2(12):2803-30. doi: 10.3390/v2122803. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Viruses. 2010. PMID: 21994641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balzarini, J., C. Pannecouque, L. Naesens, G. Andrei, R. Snoeck, E. De Clercq, D. Hocková, and A. Holý. 2004. 6-[2-(Phosphonomethoxy)alkoxy]-2,4-diaminopyrimidines: a new class of acyclic pyrimidine nucleoside phosphonates with antiviral activity. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 23:1321-1327. - PubMed
-
- Crumbie, A. 1998. The orf virus: a disease of the farming community. Community Nurse 4:44-45. - PubMed
-
- De Clercq, E., T. Sakuma, M. Baba, R. Pauwels, J. Balzarini, I. Rosenberg, and A. Holý. 1987. Antiviral activity of phosphonylmethoxyalkyl derivatives of purine and pyrimidines. Antivir. Res. 8:261-272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

