Lack of effect of experimental hypovolemia on imipenem muscle distribution in rats assessed by microdialysis
- PMID: 16304160
- PMCID: PMC1315960
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.12.4974-4979.2005
Lack of effect of experimental hypovolemia on imipenem muscle distribution in rats assessed by microdialysis
Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the influence of hypovolemia on the distribution of imipenem in muscle extracellular fluid determined by microdialysis in awake rats. Microdialysis probes were inserted into the jugular vein and hind leg muscle. Imipenem recoveries in muscle and blood were determined in each rat by retrodialysis by drug before drug administration. Hypovolemia was induced by removing 40% of the initial blood volume over 30 min. Imipenem was infused intravenously at a dose of 70 mg . kg(-1) over 30 min, and microdialysis samples were collected for 120 min from hypovolemic (n = 8) and control (n = 8) rats. The decay of the free concentrations in blood and muscle with time were monoexponential, and the concentration profiles in muscle and blood were virtually superimposed in both groups. Accordingly, the ratios of the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) for tissue (muscle) to the AUC for blood were always virtually equal to 1. Hypovolemia induced a 23% decrease in the clearance (P < 0.05) of imipenem, with no statistically significant alteration of its volume of distribution. This study showed that imipenem elimination was altered in hypovolemic rats, probably due to decreased renal blood flow, but its distribution characteristics were not. In particular, free imipenem concentrations in blood and muscle were always virtually identical.
Figures
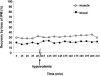
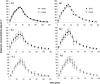
References
-
- Araki, H., N. Ogake, R. Tsuneda, S. Minami, Y. Watanabe, I. Tamai, and A. Tsuji. 2002. Muscle distribution of antimicrobial agents after a single intravenous administration to rats. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 17:237-244. - PubMed
-
- Brunner, M., T. Pernerstorfer, B. X. Mayer, H. G. Eichler, and M. Müller. 2000. Surgery and intensive care procedures affect the target site distribution of piperacillin. Crit. Care Med. 28:1754-1759. - PubMed
-
- Dalla Costa, T., A. Nolting, A. Kovar, and H. Derendorf. 1998. Determination of free interstitial concentrations of piperacillin-tazobactam combinations by microdialysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 42:769-778. - PubMed
-
- Davis, B., and T. Morris. 1993. Physiological parameters in laboratary animals and humans. Pharm. Res. 10:1093-1095. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

