Comparison of the fungicidal activities of caspofungin and amphotericin B against Candida glabrata
- PMID: 16304162
- PMCID: PMC1315975
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.12.4989-4992.2005
Comparison of the fungicidal activities of caspofungin and amphotericin B against Candida glabrata
Abstract
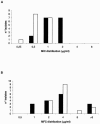
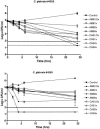
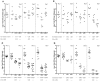
We investigated the fungicidal activity of caspofungin (CAS) and amphotericin B (AMB) against 16 clinical isolates of Candida glabrata. The minimum fungicidal concentrations (MFCs) of CAS were similar to those of AMB, ranging from 2.0 to >8.0 microg/ml. Time-kill assays performed on selected isolates showed that AMB was fungicidal at concentrations four times the MIC while CAS was not. A neutropenic-mouse model of disseminated infection was utilized to determine the residual fungal kidney burden. While doses as low as 0.3 and 1 mg/kg of body weight/day of CAS and AMB, respectively, were effective at reducing the counts with respect to controls, organ sterilization was reached when both drugs were administered at 5 mg/kg/day. Our study reveals that, similar to AMB, CAS has the potential for a fungicidal effect in vivo against this difficult-to-treat fungal pathogen.
Figures
References
-
- Bartizal, K., C. J. Gill, G. K. Abruzzo, A. M. Flattery, L. Kong, P. M. Scott, J. G. Smith, C. E. Leighton, A. Bouffard, J. F. Dropinski, and J. Balkovec. 1997. In vitro preclinical evaluation studies with the echinocandin antifungal MK-0991 (L-743,872). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41:2326-2332. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cantón, E., J. Pemán, A. Viudes, G. Quindós, M. Gobernado, and A. Espinel-Ingroff. 2003. Minimum fungicidal concentrations of amphotericin B for bloodstream Candida species. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 45:203-206. - PubMed
-
- Colombo, A. L., J. Perfect, M. DiNubile, K. Bartizal, M. Motyl, P. Hicks, R. Lupinacci, C. Sable, and N. Kartsonis. 2003. Global distribution and outcomes for Candida species causing invasive candidiasis: results from an international randomized double-blind study of caspofungin versus amphotericin B for the treatment of invasive candidiasis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 22:470-474. - PubMed
-
- Deresinski, S. C., and D. A. Stevens. 2003. Caspofungin. Clin. Infect. Dis. 36:1445-1457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

