Pitfalls in estimating piperaquine elimination
- PMID: 16304183
- PMCID: PMC1315981
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.12.5127-5128.2005
Pitfalls in estimating piperaquine elimination
Abstract
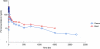
By using a sensitive new assay, the terminal elimination half-life of the antimalarial piperaquine in a healthy volunteer was estimated to be 33 days, which is longer than estimated previously. This result illustrates the importance of extended sampling duration and sensitive assay methodologies in characterizing the disposition of slowly eliminated antimalarial drugs.
Figures

References
-
- Ashley, E. A., S. Krudsood, L. Phaiphun, S. Srivilairit, R. McGready, W. Leowattana, R. Hutagalung, P. Wilairatana, A. Brockman, S. Looareesuwan, F. Nosten, and N. J. White. 2004. Randomized, controlled dose-optimization studies of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for the treatment of uncomplicated multidrug-resistant falciparum malaria in Thailand. J. Infect. Dis. 190:1773-1782. - PubMed
-
- Frisk-Holmberg, M., Y. Bergqvist, E. Termond, and B. Domeij-Nyberg. 1984. The single dose kinetics of chloroquine and its major metabolite desethylchloroquine in healthy subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 26:521-530. - PubMed
-
- Gustafsson, L. L., L. Rombo, G. Alvan, A. Bjorkman, M. Lind, and O. Walker. 1983. On the question of dose-dependent chloroquine elimination of a single oral dose. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 34:383-385. - PubMed
-
- Lindegårdh, N., M. Ashton, and Y. Bergqvist. 2003. Automated solid-phase extraction method for the determination of piperaquine in whole blood by rapid liquid chromatography. Ther. Drug Monit. 25:544-551. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

