Caspofungin and liposomal amphotericin B therapy of experimental murine scedosporiosis
- PMID: 16304187
- PMCID: PMC1315953
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.12.5139-5141.2005
Caspofungin and liposomal amphotericin B therapy of experimental murine scedosporiosis
Abstract
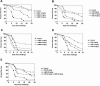
Immunosuppressed mice were infected intravenously with conidia of Scedosporium prolificans. Treatment was begun 1 day later with liposomal amphotericin B, caspofungin, or both drugs initiated concurrently. Amphotericin B and caspofungin were each effective, but combined therapy did not appear to offer advantages over liposomal amphotericin B alone.
Figures

References
-
- Berenguer, J., J. L. Rodriguez-Tudela, C. Richard, M. Alvarez, M. A. Sanz, L. Gaztelurrutia, J. Ayats, J. V. Martinez-Suarez, and the Scedosporium prolificans Study Group. 1997. Deep infections caused by Scedosporium prolificans. A report on 16 cases in Spain and a review of the literature. Medicine 76:256-265. - PubMed
-
- Husain, S., B. D. Alexander, P. Munoz, R. K. Avery, S. Houston, T. Pruett, R. Jacobs, E. A. Dominguez, J. G. Tollemar, K. Baumgarten, C. M. Yu, M. M. Wagener, P. Linden, S. Kusne, and N. Singh. 2003. Opportunistic mycelial fungal infections in organ transplant recipients: emerging importance of non-Aspergillus mycelial fungi. Clin. Infect. Dis. 37:221-229. - PubMed
-
- Husain, S., P. Munoz, G. Forrest, B. D. Alexander, J. Somani, K. Brennan, M. M. Wagener, and N. Singh. 2005. Infections due to Scedosporium apiospermum and Scedosporium prolificans in transplant recipients: clinical characteristics and impact of antifungal therapy on outcome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 40:89-99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

