Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 is expressed prior to penetrating the intestine
- PMID: 16304611
- PMCID: PMC1287911
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0010032
Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 is expressed prior to penetrating the intestine
Abstract
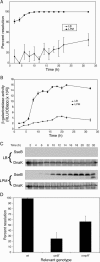
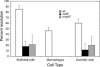
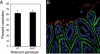
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is a facultative intracellular pathogen that causes disease in mice that resembles human typhoid. Typhoid pathogenesis consists of distinct phases in the intestine and a subsequent systemic phase in which bacteria replicate in macrophages of the liver and spleen. The type III secretion system encoded by Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 (SPI-2) is a major virulence factor contributing to the systemic phase of typhoid pathogenesis. Understanding how pathogens regulate virulence mechanisms in response to the environment, including different host tissues, is key to our understanding of pathogenesis. A recombinase-based in vivo expression technology system was developed to assess SPI-2 expression during murine typhoid. SPI-2 expression was detectable at very early times in bacteria that were resident in the lumen of the ileum and was independent of active bacterial invasion of the epithelium. We also provide direct evidence for the regulation of SPI-2 by the Salmonella transcription factors ompR and ssrB in vivo. Together these results demonstrate that SPI-2 expression precedes penetration of the intestinal epithelium. This induction of expression precedes any documented SPI-2-dependent phases of typhoid and may be involved in preparing Salmonella to successfully resist the antimicrobial environment encountered within macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
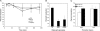
References
-
- Vazquez-Torres A, Jones-Carson J, Baumler AJ, Falkow S, Valdivia R, et al. Extraintestinal dissemination of Salmonella by CD18-expressing phagocytes. Nature. 1999;401:804–808. - PubMed
-
- Rescigno M, Urbano M, Valzasina B, Francolini M, Rotta G, et al. Dendritic cells express tight junction proteins and penetrate gut epithelial monolayers to sample bacteria. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:361–367. - PubMed
-
- Salcedo SP, Noursadeghi M, Cohen J, Holden DW. Intracellular replication of Salmonella typhimurium strains in specific subsets of splenic macrophages in vivo. Cell Microbiol. 2001;3:587–597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

