Muscarinic receptor transcript and protein density in hypertrophied and atrophied rat urinary bladder
- PMID: 16304675
- PMCID: PMC3277085
- DOI: 10.1002/nau.20180
Muscarinic receptor transcript and protein density in hypertrophied and atrophied rat urinary bladder
Abstract
Aims: Our previous studies showed that bladder hypertrophy shifts the muscarinic receptor subtype mediating contraction from M(3) towards M(2) along with increased M(2) and decreased M(3) protein concentration. We quantified mRNA for M(1) through M(5) receptors to determine whether the changes in M(2) and M(3) protein levels was due to changes in transcription.
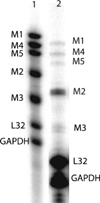
Methods: Bladder hypertrophy was induced by bladder outlet obstruction (BOO), major pelvic ganglion electrocautery (DEN), and major pelvic ganglion decentralization (DEC). Bladder atrophy was induced by ureteral diversion (DIV). Additional groups included denervated and diverted (DEN-DIV), sham operated (SHAM), and normal (NOR) controls. Transcripts were quantified using a multiplex ribonuclease protection assay (RPA) and receptor protein density was determined by immunoprecipitation. Receptor transcripts were expressed per unit total RNA.
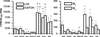
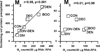
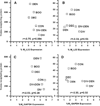
Results: Although all five receptor subtype transcripts were detected in all experimental groups, the densities of M(1), M(4), and M(5) were much lower than for the M(2) and M(3) subtype. There were more M(2) receptor transcripts than all the others, consistent with M(2) protein determinations. M(2) transcripts were significantly increased in DEN and BOO bladders. Surprisingly, M(3) transcripts were also significantly increased in BOO. There was a significant correlation (r=0.98, P<0.001) between protein density and transcript density for the M(2) but not the M(3) receptor among the different experimental groups.
Conclusions: Changes in mRNA concentration are reflected by changes in protein density for the M(2) receptor but not for the M(3) receptor. Extrapolation of functional effects from transcript density data is invalid for M(3) mediated bladder contractions.
(c) 2005 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hypertrophy changes the muscarinic receptor subtype mediating bladder contraction from M3 toward M2.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2003 Sep;285(3):R701-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00009.2003. Epub 2003 May 22. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12763741 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of bladder muscarinic receptor subtypes by experimental pathologies.Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2006 Jul;26(3):311-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.2006.00377.x. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16879497 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic receptor density in the rat urinary bladder after denervation, hypertrophy and urinary diversion.Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 1986 Oct;59(4):306-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1986.tb00174.x. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 1986. PMID: 3541495
-
On the muscarinic receptors in the urinary bladder and the putative subclassification of muscarinic receptors.Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 1986;59 Suppl 1:1-45. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 1986. PMID: 3524114 Review.
-
[Changes in the receptor profile of the aging bladder].Urologe A. 2004 May;43(5):535-41. doi: 10.1007/s00120-004-0573-y. Urologe A. 2004. PMID: 15112040 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Muscarinic receptor subtype mRNA expression in the human prostate: association with age, pathological diagnosis, prostate size, or potentially interfering medications?Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014 Feb;387(2):207-14. doi: 10.1007/s00210-013-0934-4. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24193354
-
Temporal morphological and functional impact of complete urinary diversion on the bladder: a model of bladder disuse in rats.J Urol. 2010 Nov;184(5):2179-85. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2010.06.090. Epub 2010 Sep 17. J Urol. 2010. PMID: 20850838 Free PMC article.
-
Blebbistain, a myosin II inhibitor, as a novel strategy to regulate detrusor contractility in a rat model of partial bladder outlet obstruction.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025958. Epub 2011 Oct 7. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22016792 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of bladder outlet obstruction on properties of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in rat bladder.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 May;298(5):R1310-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00523.2009. Epub 2010 Mar 3. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20200132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bas A, Forsberg G, Hammarstrom S, et al. Utility of the housekeeping genes 18S rRNA, beta-actin and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase for normalization in real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis of gene expression in human T lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 2004;59:566–573. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

