Humoral and cellular immune response to RNA immunization with flavivirus replicons derived from tick-borne encephalitis virus
- PMID: 16306582
- PMCID: PMC1316042
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.24.15107-15113.2005
Humoral and cellular immune response to RNA immunization with flavivirus replicons derived from tick-borne encephalitis virus
Abstract
A new vaccination principle against flaviviruses, based on a tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) self-replicating noninfectious RNA vaccine that produces subviral particles, has recently been introduced (R. M. Kofler, J. H. Aberle, S. W. Aberle, S. L. Allison, F. X. Heinz, and C. W. Mandl, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 7:1951-1956, 2004). In this study, we evaluated the potential of the self-replicating RNA vaccine in mice in comparison to those of live, attenuated vaccines and a formalin-inactivated whole-virus vaccine (ImmunInject). For this purpose, mice were immunized using gene gun-mediated application of the RNA vaccine and tested for CD8+ T-cell responses, long-term duration, neutralizing capacity, and isotype profile of specific antibodies and protection against lethal virus challenge. We demonstrate that the self-replicating RNA vaccine induced a broad-based, humoral and cellular (Th1 and CD8+ T-cell response) immune response comparable to that induced by live vaccines and that it protected mice from challenge. Even a single immunization with 1 microg of the replicon induced a long-lasting antibody response, characterized by high neutralizing antibody titers, which were sustained for at least 1 year. Nevertheless, it was possible to boost this response further by a second injection with the RNA vaccine, even in the presence of a concomitant CD8+ T-cell response. In this way it was possible to induce a balanced humoral and cellular immune response, similar to infection-induced immunity but without the safety hazards of infectious agents. The results also demonstrate the value of TBEV replicon RNA for inducing protective long-lasting antiviral responses.
Figures


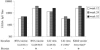
References
-
- Aberle, J. H., S. W. Aberle, S. L. Allison, K. Stiasny, M. Ecker, C. W. Mandl, R. Berger, and F. X. Heinz. 1999. A DNA immunization model study with constructs expressing the tick-borne encephalitis virus envelope protein E in different physical forms. J. Immunol. 163:6756-6761. - PubMed
-
- Ashok, M. S., and P. N. Rangarajan. 1999. Immunization with plasmid DNA encoding the envelope glycoprotein of Japanese encephalitits virus confers significant protection against intracerebral viral challenge without inducing detectable antiviral antibodies. Vaccine 18:68-75. - PubMed
-
- Burke, D. S., and T. P. Monath. 2001. Flaviviruses, p. 1043-1125. In D. M. Knipe and P. M. Howley (ed.), Fields virology, 4th ed. Lippincott-Raven Publisher, New York, N.Y.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

