Blockade of neutrophil elastase attenuates severe liver injury in hepatitis B transgenic mice
- PMID: 16306586
- PMCID: PMC1315990
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.24.15142-15150.2005
Blockade of neutrophil elastase attenuates severe liver injury in hepatitis B transgenic mice
Abstract
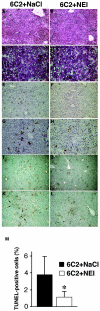
Serine proteinases produced by polymorphonuclear neutrophils play important roles in neutrophil-mediated tissue injury at inflammatory sites. Although neutrophil recruitment to the liver has been shown to be involved in the exacerbation of liver inflammation, the function of neutrophil elastase (NE) in liver injury remains unclear. Here, we found that administration of an NE inhibitor (NEI) reduced serum alanine aminotransferase (sALT) activity and inflammatory cell infiltration into the liver from 8 to 24 h after injection of antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) into hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Furthermore, the NEI treatment reduced the expressions of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the liver and tumor necrosis factor alpha production by macrophages. In addition, the NEI treatment suppressed the mRNA expressions of CC chemokine ligand 3 (CCL-3), CCL-4, and macrophage inflammatory protein 2 (MIP-2) in neutrophils in the liver at 8 h after the CTL injection. In support of these results, we confirmed that administration of anti-CCL-3, anti-CCL-4, and anti-MIP-2 monoclonal antibodies suppressed sALT activity and leukocyte migration into the liver. In conclusion, the present results suggest that NE contributes to the early step of the inflammatory cascade in acute viral hepatitis and that NEIs may have potential as therapeutic drugs against acute severe viral hepatitis.
Figures
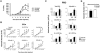



Similar articles
-
Role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in hepatitis B virus-specific cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte-induced liver injury.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2006 Mar;13(3):415-9. doi: 10.1128/CVI.13.3.415-419.2006. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16522786 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil elastase inhibitor (sivelestat) attenuates subsequent ventilator-induced lung injury in mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Sep 24;571(1):62-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.05.053. Epub 2007 Jun 9. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17599828
-
Neutrophil recruitment in immunized mice depends on MIP-2 inducing the sequential release of MIP-1alpha, TNF-alpha and LTB(4).Eur J Immunol. 2006 Aug;36(8):2025-34. doi: 10.1002/eji.200636057. Eur J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16856209
-
Anti-inflammatory activity of neutrophil elastase inhibitors.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2003 May;4(5):556-65. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12833649 Review.
-
Intrahepatic T cells in hepatitis B: viral control versus liver cell injury.J Exp Med. 2000 Apr 17;191(8):1263-8. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.8.1263. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10770794 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Fibrinogen alpha C chain 5.9 kDa fragment (FIC5.9), a biomarker for various pathological conditions, is produced in post-blood collection by fibrinolysis and coagulation factors.Clin Proteomics. 2016 Oct 7;13:27. doi: 10.1186/s12014-016-9129-6. eCollection 2016. Clin Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27761105 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CD44 in CTL-induced acute liver injury in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice.J Gastroenterol. 2009;44(3):218-27. doi: 10.1007/s00535-008-2300-8. Epub 2009 Feb 13. J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19214666
-
Molecular MR Imaging of Myeloperoxidase Distinguishes Steatosis from Steatohepatitis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Radiology. 2017 Aug;284(2):390-400. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017160588. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Radiology. 2017. PMID: 28358240 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil-Induced Liver Injury and Interactions Between Neutrophils and Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells.Inflammation. 2021 Aug;44(4):1246-1262. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01442-x. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33649876 Review.
-
Macrophage scavenger receptor 1 contributes to pathogenesis of fulminant hepatitis via neutrophil-mediated complement activation.J Hepatol. 2018 Apr;68(4):733-743. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.010. Epub 2017 Nov 14. J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29154963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ando, K., L. G. Guidotti, A. Cerny, T. Ishikawa, and F. V. Chisari. 1994. CTL access to tissue antigen is restricted in vivo. J. Immunol. 153:482-488. - PubMed
-
- Belaaouaj, A., R. McCarthy, M. Baumann, Z. Gao, T. J. Ley, S. N. Abraham, and S. D. Shapiro. 1998. Mice lacking neutrophil elastase reveal impaired host defense against gram negative bacterial sepsis. Nat. Med. 4:615-618. - PubMed
-
- Chen, H. M., J. C. Chen, M. H. Shyr, M. F. Chen, T. L. Hwang, L. L. Fan, T. Y. Chi, and C. P. Chi. 1999. Neutrophil elastase inhibitor (ONO-5046) attenuates reperfusion-induced hepatic microcirculatory derangement, energy depletion and lipid peroxidation in rats. Shock 12:462-467. - PubMed
-
- Chertov, O., D. Yang, O. M. Howard, and J. J. Oppenheim. 2000. Leukocyte granule proteins mobilize innate host defenses and adaptive immune responses. Immunol. Rev. 177:68-78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

