Transcription program of red sea bream iridovirus as revealed by DNA microarrays
- PMID: 16306587
- PMCID: PMC1316049
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.24.15151-15164.2005
Transcription program of red sea bream iridovirus as revealed by DNA microarrays
Abstract
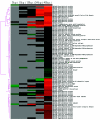
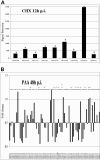
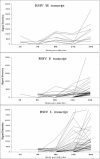
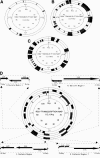
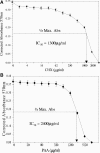
Red sea bream iridovirus (RSIV) has been identified as the causative agent of a serious disease in red sea bream and at least 30 other marine fish species. We developed a viral DNA microarray containing 92 putative open reading frames of RSIV to monitor the viral gene transcription program over the time course of an in vitro infection and to classify RSIV transcripts into temporal kinetic expression classes. The microarray analysis showed that viral genes commenced expression as early as 3 h postinfection (p.i.) and this was followed by a rapid escalation of gene expression from 8 h p.i. onwards. Based on the expression of some enzymes associated with viral DNA replication, the DNA replication of RSIV appeared to begin at around 8 h p.i. in infected cells in vitro. Using a de novo protein synthesis inhibitor (cycloheximide) and a viral DNA replication inhibitor (phosphonoacetic acid), 87 RSIV transcripts could be classified into three temporal kinetic classes: nine immediate-early (IE), 40 early (E), and 38 late (L) transcripts. The gene expression of RSIV occurred in a temporal kinetic cascade with three stages (IE, E, and L). Although the three classes of transcripts were distributed throughout the RSIV genome, E transcripts appeared to cluster in at least six discrete regions and L transcripts appeared to originate from seven discrete regions. The microarray data were statistically confirmed by using a t test, and were also clustered into groups based on similarity in the gene expression patterns by using a cluster program.
Figures

References
-
- Bowtell, D., and J. Sambrook (ed.). 2002. DNA microarrays: a molecular cloning manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
-
- Byon, J. Y., T. Ohira, I. Hirono, and T. Aoki. 2005. Use of a cDNA microarray to study immunity against viral hemorrhagic septicemia (VHS) in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) following DNA vaccination. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 18:135-147. - PubMed
-
- Caipang, C. M., I. Hirono, and T. Aoki. 2003. Development of a real-time PCR assay for the detection and quantification of red sea bream Iridovirus (RSIV). Fish Pathol. 38:1-7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

