An epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)dodecanoic acid (AUDA), reduces ischemic cerebral infarct size in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 16306811
- PMCID: PMC1444897
- DOI: 10.1097/01.fjc.0000189600.74157.6d
An epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)dodecanoic acid (AUDA), reduces ischemic cerebral infarct size in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats
Abstract
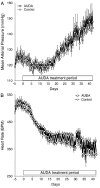
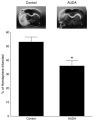
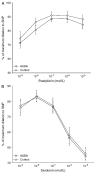
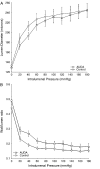
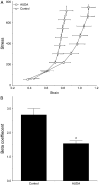
Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) inhibitors have been demonstrated to have cardiovascular protective actions. This hydrolase enzyme converts fatty acid epoxides to their corresponding diols, and this conversion can alter the biologic activity of these metabolites. We hypothesized that 12-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)dodecanoic acid (AUDA), a sEH inhibitor, would protect stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats from cerebral ischemia. AUDA was administered to 6-week-old male rats for 6 weeks, during which blood pressure was measured by telemetry. Cerebral ischemia was induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion, the size of the cerebral infarct was assessed after 6 hours of ischemia, and the results were expressed as a percentage of the hemisphere infarcted (%HI). Vascular structure and function were assessed using a pressurized arteriograph. Plasma levels of AUDA at the end of the treatment period averaged 5.0 +/- 0.4 ng/mL, and the urinary excretion rate was 99 +/- 21 ng/d. AUDA-treated rats had significantly smaller cerebral infarcts than control rats (36 +/- 4% vs 53 +/- 4% HI, treated versus control, P < 0.05, n = 6). This difference occurred independently of changes in blood pressure. AUDA treatment increased the passive compliance of the cerebral vessels but had no effect on vascular structure. The results of this study provide novel evidence suggesting that the sEH inhibitor AUDA is a possible therapeutic agent for ischemic stroke.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Soluble epoxide inhibition is protective against cerebral ischemia via vascular and neural protection.Am J Pathol. 2009 Jun;174(6):2086-95. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080544. Epub 2009 May 12. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19435785 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, AUDA, prevents early salt-sensitive hypertension.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:3480-7. doi: 10.2741/2942. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508449
-
Administration of a substituted adamantyl urea inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase protects the kidney from damage in hypertensive Goto-Kakizaki rats.Clin Sci (Lond). 2009 Jan;116(1):61-70. doi: 10.1042/CS20080039. Clin Sci (Lond). 2009. PMID: 18459944 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase: a new target for cardioprotection.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009 Mar;10(3):253-8. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19333883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular therapeutic aspects of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors.Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2006 Summer;24(2):169-88. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2006.00169.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2006. PMID: 16961727 Review.
Cited by
-
20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid Inhibition by HET0016 Offers Neuroprotection, Decreases Edema, and Increases Cortical Cerebral Blood Flow in a Pediatric Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest Model in Rats.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015 Nov;35(11):1757-63. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.117. Epub 2015 Jun 10. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015. PMID: 26058691 Free PMC article.
-
1-(1-acetyl-piperidin-4-yl)-3-adamantan-1-yl-urea (AR9281) as a potent, selective, and orally available soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor with efficacy in rodent models of hypertension and dysglycemia.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Feb 1;21(3):983-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.12.042. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011. PMID: 21211973 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in lung ischemia-reperfusion injury.Microcirculation. 2010 Feb;17(2):137-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1549-8719.2009.00013.x. Microcirculation. 2010. PMID: 20163540 Free PMC article.
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids enhance axonal growth in primary sensory and cortical neuronal cell cultures.J Neurochem. 2011 May;117(4):632-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07139.x. Epub 2011 Jan 24. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 21155804 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting vascular inflammation in ischemic stroke: Recent developments on novel immunomodulatory approaches.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Aug 15;833:531-544. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.06.028. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29935175 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coyle P, Jokelainen PT. Differential outcome to middle cerebral artery occlusion in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRSP) and Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats. Stroke. 1983;14:605–611. - PubMed
-
- Coyle P, Heistad DD. Blood flow through cerebral and collateral vessels one month after middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke. 1987;18:407–411. - PubMed
-
- Zhao X, Yamamoto T, Newman JW, et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition protects the kidney from hypertension-induced damage. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:12442–12445. - PubMed
-
- Yu Z, Xu F, Huse LM, et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase regulates hydrolysis of vasoactive epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Circ Res. 2000;87:992–998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

