Long term efficacy and safety of adalimumab plus methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: ARMADA 4 year extended study
- PMID: 16308341
- PMCID: PMC1798163
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2005.044404
Long term efficacy and safety of adalimumab plus methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: ARMADA 4 year extended study
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of adalimumab plus methotrexate (MTX) given for up to 4 years in patients with active, longstanding rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods: Patients responding inadequately to MTX were entered into a 24 week, controlled study (ARMADA) with adalimumab plus MTX or placebo plus MTX, and some were enrolled in a subsequent open label extension. The efficacy and safety of treatment were evaluated. Additional analyses were made for those patients whose corticosteroid and/or MTX dosages were adjusted during the extension.
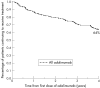
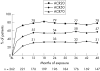
Results: Of 271 patients in the original ARMADA trial, 262 received at least one dose of adalimumab and were evaluated. At the time of analysis, 162/262 (62%) patients had remained in the study and received treatment for a mean of 3.4 years. Withdrawals were for lack of efficacy (8%), adverse events (12%), and other reasons (18%). In 147 patients who completed 4 years' treatment, efficacy achieved at 6 months was maintained. At 4 years, 78%, 57%, and 31% had achieved ACR20/50/70; 43% achieved clinical remission (DAS28 <2.6); and 22% had no physical function abnormalities (HAQ = 0). Results were similar for 196 patients who received treatment for 2-4 years. Efficacy was maintained in many patients when dosages were decreased (corticosteroids (51/81 (63%) patients), MTX (92/217 (42%)), or both (25/217 (12%))). Serious adverse events were comparable during open label treatment and the controlled phase. Serious infections occurring during open label treatment and the blinded period were similar (2.03 v 2.30 events per 100 patient-years, respectively).
Conclusions: Adalimumab plus MTX sustained clinical response and remission in patients with RA during 4 years. The safety profile during the first 6 months was similar to that after 4 years' follow up. Reduction of corticosteroid and/or MTX dosages did not adversely affect long term efficacy.
References
-
- Choy E, Panayi G. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2001344907–916. - PubMed
-
- Lee D, Weinblatt M. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2001358903–911. - PubMed
-
- O'Dell J. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 20043502591–2602. - PubMed
-
- Furst D E, Breedveld F C, Kalden J R, Smolen J S, Burmester G R, Bijlsma J W.et al Updated consensus statement on biological agents, specifically tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) blocking agents and interleukin‐1 receptor antagonists (IL‐1ra), for the treatment of rheumatic diseases, 2005. Ann Rheum Dis 200564(suppl IV)iv2–NaN14. - PMC - PubMed