3-D structural and functional characterization of the purified KATP channel complex Kir6.2-SUR1
- PMID: 16308567
- PMCID: PMC1356316
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600877
3-D structural and functional characterization of the purified KATP channel complex Kir6.2-SUR1
Abstract
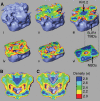
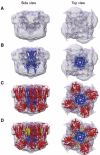
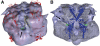
ATP-sensitive potassium (K(ATP)) channels conduct potassium ions across cell membranes and thereby couple cellular energy metabolism to membrane electrical activity. Here, we report the heterologous expression and purification of a functionally active K(ATP) channel complex composed of pore-forming Kir6.2 and regulatory SUR1 subunits, and determination of its structure at 18 A resolution by single-particle electron microscopy. The purified channel shows ATP-ase activity similar to that of ATP-binding cassette proteins related to SUR1, and supports Rb(+) fluxes when reconstituted into liposomes. It has a compact structure, with four SUR1 subunits embracing a central Kir6.2 tetramer in both transmembrane and cytosolic domains. A cleft between adjacent SUR1s provides a route by which ATP may access its binding site on Kir6.2. The nucleotide-binding domains of adjacent SUR1 appear to interact, and form a large docking platform for cytosolic proteins. The structure, in combination with molecular modelling, suggests how SUR1 interacts with Kir6.2.
Figures
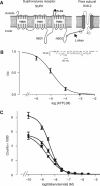
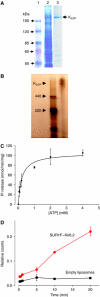
 ) or into control liposomes containing no protein (▪). Data shown are the mean±s.e.m. of three separate experiments (one protein preparation; similar results were obtained with a second protein preparation).
) or into control liposomes containing no protein (▪). Data shown are the mean±s.e.m. of three separate experiments (one protein preparation; similar results were obtained with a second protein preparation).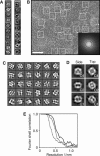
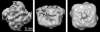
References
-
- Ashcroft FM, Gribble FM (2000) New windows on the mechanism of action of KATP channel openers. Trends Pharmacol Sci 21: 439–445 - PubMed
-
- Babenko AP, Bryan J (2002) SUR-dependent modulation of KATP channels by an N-terminal KIR6.2 peptide. Defining intersubunit gating interactions. J Biol Chem 277: 43997–44004 - PubMed
-
- Beis K, Collins RF, Ford RC, Kamis AB, Whitfield C, Naismith JH (2004) Three-dimensional structure of Wza, the protein required for translocation of group 1 capsular polysaccharide across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 279: 28227–28232 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

