P-TEFb is not an essential elongation factor for the intronless human U2 snRNA and histone H2b genes
- PMID: 16308568
- PMCID: PMC1356315
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600876
P-TEFb is not an essential elongation factor for the intronless human U2 snRNA and histone H2b genes
Abstract
Phosphorylation of Ser2 of the heptapeptide repeat of the CTD of mammalian pol II by P-TEFb is associated with productive elongation of transcription of protein-coding genes. Here, we show that the CTD of pol II transcribing the human U2 snRNA genes is phosphorylated on Ser2 in vivo and that both the CDK9 kinase and cyclin T components of P-TEFb are required for cotranscriptional recognition of the 3' box RNA 3' end processing signal. However, inhibitors of CDK9 do not affect transcription of the U2 genes, indicating that P-TEFb functions exclusively as an RNA processing factor in expression of these relatively short, intronless genes. We also show that inhibition of CDK9 does not adversely affect either transcription of an intron-less, replication-activated histone H2b gene or recognition of the histone gene-specific U7-dependent RNA 3' end formation signal. These results emphasize that the role of P-TEFb as an activator of transcription elongation can be separated from its role in RNA processing and that neither function is universally required for expression of mammalian pol II-dependent genes.
Figures
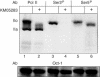
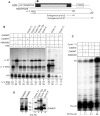
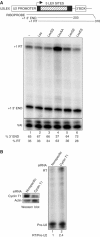
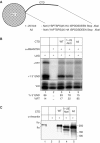
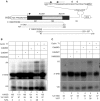
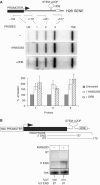
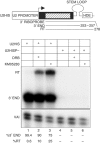
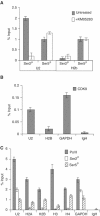
References
-
- Ahn SH, Kim M, Buratowski S (2004) Phosphorylation of serine 2 within the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain couples transcription and 3′ end processing. Mol Cell 13: 67–76 - PubMed
-
- Chao SH, Price DH (2001) Flavopiridol inactivates P-TEFb and blocks most RNA polymerase II transcription in vivo. J Biol Chem 276: 31793–31799 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

