A promiscuous liaison between IL-15 receptor and Axl receptor tyrosine kinase in cell death control
- PMID: 16308569
- PMCID: PMC1356322
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600874
A promiscuous liaison between IL-15 receptor and Axl receptor tyrosine kinase in cell death control
Retraction in
-
Retraction. A promiscuous liaison between IL-15 receptor and Axl receptor tyrosine kinase in cell death control.EMBO J. 2011 Feb 2;30(3):627. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.7. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21285977 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
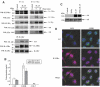
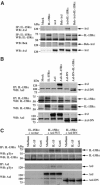
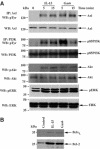
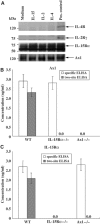
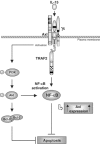
Discrimination between cytokine receptor and receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling pathways is a central paradigm in signal transduction research. Here, we report a 'promiscuous liaison' between both receptors that enables interleukin (IL)-15 to transactivate the signaling pathway of a tyrosine kinase. IL-15 protects murine L929 fibroblasts from tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha)-induced cell death, but fails to rescue them upon targeted depletion of the RTK, Axl; however, Axl-overexpressing fibroblasts are TNFalpha-resistant. IL-15Ralpha and Axl colocalize on the cell membrane and co-immunoprecipitate even in the absence of IL-15, whereby the extracellular part of Axl proved to be essential for Axl/IL-15Ralpha interaction. Most strikingly, IL-15 treatment mimics stimulation by the Axl ligand, Gas6, resulting in a rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of both Axl and IL-15Ralpha, and activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. This is also seen in mouse embryonic fibroblasts from wild-type but not Axl-/- or IL-15Ralpha-/- mice. Thus, IL-15-induced protection from TNFalpha-mediated cell death involves a hitherto unknown IL-15 receptor complex, consisting of IL-15Ralpha and Axl RTK, and requires their reciprocal activation initiated by ligand-induced IL-15Ralpha.
Figures




References
-
- Allen MP, Zeng C, Schneider K, Xiong X, Meintzer MK, Bellosta P, Basilico C, Varnum B, Heidenreich KA, Wiermann ME (1999) Growth arrest-specific gene 6 (Gas6)/adhesion related kinase (Ark) signaling promotes gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuronal survival via extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Akt. Mol Endocrinol 13: 191–201 - PubMed
-
- Bellosta P, Zhang Q, Goff SP, Basilico C (1997) Signaling through the Ark tyrosine kinase receptor protects from apoptosis in the absence of growth stimulation. Oncogene 15: 2387–2397 - PubMed
-
- Bennasroune A, Gardin A, Aunis D, Cremel G, Hubert P (2004) Tyrosine kinase receptors as attractive targets of cancer therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 50: 23–38 - PubMed
-
- Brandt K, Bulfone-Paus S, Foster DC, Rückert R (2003) Interleukin-21 inhibits dendritic cell activation and maturation. Blood 102: 4090–4098 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

