Cross-reactive influenza virus-specific CD8+ T cells contribute to lymphoproliferation in Epstein-Barr virus-associated infectious mononucleosis
- PMID: 16308574
- PMCID: PMC1288832
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI25078
Cross-reactive influenza virus-specific CD8+ T cells contribute to lymphoproliferation in Epstein-Barr virus-associated infectious mononucleosis
Abstract
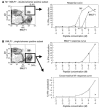
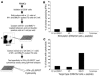
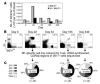
The marked proliferation of activated CD8+ T cells is pathognomonic of EBV-associated infectious mononucleosis (IM), common in young adults. Since the diversity and size of the memory CD8+ T cell population increase with age, we questioned whether IM was mediated by the reactivation of memory CD8+ T cells specific to previously encountered pathogens but cross-reactive with EBV. Of 8 HLA-A2+ IM patients, 5 had activated T cells specific to another common virus, as evidenced by a significantly higher number of peripheral blood influenza A virus M1(58-66)-specific T cells compared with healthy immune donors. Two patients with an augmented M1 response had tetramer-defined cross-reactive cells recognizing influenza M1 and EBV-BMLF1(280-288), which accounted for up to one-third of their BMLF1-specific population and likely contributed to a skewed M1-specific T cell receptor repertoire. These epitopes, with only 33% sequence similarity, mediated differential effects on the function of the cross-reactive T cells, which may contribute to alterations in disease outcome. EBV could potentially encode an extensive pool of T cell epitopes that activate other cross-reactive memory T cells. Our results support the concept that cross-reactive memory CD8+ T cells activated by EBV contribute to the characteristic lymphoproliferation of IM.
Figures



References
-
- Hoagland RJ. Infectious mononucleosis. Prim. Care. 1975;2:295–307. - PubMed
-
- Young LS, Rickinson AB. Epstein-Barr virus: 40 years on. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2004;4:757–768. - PubMed
-
- Rea TD, Russo JE, Katon W, Ashley RL, Buchwald DS. Prospective study of the natural history of infectious mononucleosis caused by Epstein-Barr virus. J. Am. Board Fam. Pract. 2001;14:234–242. - PubMed
-
- Auwaerter PG. Infectious mononucleosis in middle age. JAMA. 1999;281:454–459. - PubMed
-
- Axelrod P, Finestone AJ. Infectious mononucleosis in older adults. Am. Fam. Physician. 1990;42:1599–1606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

