Biochemical analysis of the EJC reveals two new factors and a stable tetrameric protein core
- PMID: 16314458
- PMCID: PMC1370875
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2155905
Biochemical analysis of the EJC reveals two new factors and a stable tetrameric protein core
Abstract
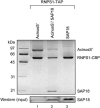
The multiprotein exon junction complex (EJC) is deposited on mRNAs upstream of exon-exon junctions as a consequence of pre-mRNA splicing. In mammalian cells, this complex serves as a key modulator of spliced mRNA metabolism. To date, neither the complete composition nor the exact assembly pathway of the EJC has been entirely elucidated. Using in vitro splicing and a two-step chromatography procedure, we have purified the EJC and analyzed its components by mass spectrometry. In addition to finding most of the known EJC factors, we identified two novel EJC components, Acinus and SAP18. Heterokaryon analysis revealed that SAP18 is a shuttling protein whereas Acinus is restricted to the nucleus. In MS2 tethering assays Acinus stimulated gene expression at the RNA level, while MLN51, another EJC factor, stimulated mRNA translational efficiency. Using tandem affinity purification (TAP) of proteins overexpressed in HeLa cells, we demonstrated that Acinus binds directly to another EJC component, RNPS1, while stable association of SAP18 to form the trimeric apoptosis and splicing associated protein (ASAP) complex requires both Acinus and RNPS1. Using the same methodology, we further identified what appears to be the minimal stable EJC core, a heterotetrameric complex consisting of eIF4AIII, Magoh, Y14, and MLN51.
Figures

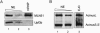
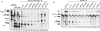




Similar articles
-
The exon junction core complex is locked onto RNA by inhibition of eIF4AIII ATPase activity.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005 Oct;12(10):861-9. doi: 10.1038/nsmb990. Epub 2005 Sep 18. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16170325
-
Association of the breast cancer protein MLN51 with the exon junction complex via its speckle localizer and RNA binding module.J Biol Chem. 2004 Aug 6;279(32):33702-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402754200. Epub 2004 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15166247
-
Transcriptome-wide modulation of splicing by the exon junction complex.Genome Biol. 2014;15(12):551. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0551-7. Genome Biol. 2014. PMID: 25476502 Free PMC article.
-
The Physiological Roles of the Exon Junction Complex in Development and Diseases.Cells. 2022 Apr 1;11(7):1192. doi: 10.3390/cells11071192. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of the exon junction complex components in the central nervous system: a mini review.Rev Neurosci. 2018 Nov 27;29(8):817-824. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2017-0113. Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29791316 Review.
Cited by
-
The kinesin motor KIF1C is a putative transporter of the exon junction complex in neuronal cells.RNA. 2022 Oct 31;29(1):55-68. doi: 10.1261/rna.079426.122. Online ahead of print. RNA. 2022. PMID: 36316088 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic mRNP Remodeling in Response to Internal and External Stimuli.Biomolecules. 2020 Sep 11;10(9):1310. doi: 10.3390/biom10091310. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32932892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CWC22-dependent pre-mRNA splicing and eIF4A3 binding enables global deposition of exon junction complexes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 May 19;43(9):4687-700. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv320. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25870412 Free PMC article.
-
The exon junction complex component Y14 modulates the activity of the methylosome in biogenesis of spliceosomal small nuclear ribonucleoproteins.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 18;286(11):8722-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.190587. Epub 2011 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21209085 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear distribution of RNA polymerase II and mRNA processing machinery in early mammalian embryos.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:681596. doi: 10.1155/2014/681596. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24868542 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ballut, L., Marchadier, B., Baguet, A., Tomasetto, C., Seraphin, B., and Le Hir, H. 2005. The exon junction core complex is locked onto RNA by inhibition of EIF4AIII ATPase activity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12: 861–869. - PubMed
-
- Conti, E. and Izaurralde, E. 2005. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: Molecular insights and mechanistic variations across species. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 17: 316–325. - PubMed
-
- Degot, S., Le Hir, H., Alpy, F., Kedinger, V., Stoll, I., Wendling, C., Seraphin, B., Rio, M.C., and Tomasetto, C. 2004. Association of the breast cancer protein MLN51 with the exon junction complex via its speckle localizer and RNA binding module. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 33702–33715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
